 |
PDBsum entry 4xoi
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Cell cycle
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of hsanillin bound with rhoa(q63l) at 2.1 angstroms resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Transforming protein rhoa. Chain: a, c. Fragment: unp residues 1-180. Synonym: rho cdna clone 12,h12. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Actin-binding protein anillin. Chain: b, d. Fragment: rbd domain, unp residues 712-981.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: rhoa, arh12, arha, rho12. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: anln.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.09Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.174
|
R-free:
|
0.206
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.Sun,R.Guan,I.-J.Lee,Y.Liu,M.Chen,J.Wang,J.Wu,Z.Chen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
L.Sun
et al.
(2015).
Mechanistic insights into the anchorage of the contractile ring by anillin and Mid1.
Dev Cell,
33,
413-426.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Jan-15
|
Release date:
|
15-Jul-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
GTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
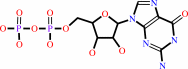 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, D:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Dev Cell
33:413-426
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanistic insights into the anchorage of the contractile ring by anillin and Mid1.
|
|
L.Sun,
R.Guan,
I.J.Lee,
Y.Liu,
M.Chen,
J.Wang,
J.Q.Wu,
Z.Chen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Anillins and Mid1 are scaffold proteins that play key roles in anchorage of the
contractile ring at the cell equator during cytokinesis in animals and fungi,
respectively. Here, we report crystal structures and functional analysis of
human anillin and S. pombe Mid1. The combined data show anillin contains
a cryptic C2 domain and a Rho-binding domain. Together with the tethering PH
domain, three membrane-associating elements synergistically bind to RhoA and
phospholipids to anchor anillin at the cleavage furrow. Surprisingly, Mid1 also
binds to the membrane through a cryptic C2 domain. Dimerization of Mid1 leads to
high affinity and preference for PI(4,5)P2, which stably anchors Mid1 at the
division plane, bypassing the requirement for Rho GTPase. These findings uncover
the unexpected general machinery and the divergent regulatory logics for the
anchorage of the contractile ring through the anillin/Mid1 family proteins from
yeast to humans.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

