 |
PDBsum entry 4xjc
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Dctp deaminase-dutpase from bacillus halodurans
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Deoxycytidine triphosphate deaminase. Chain: a, c, e, b, d, f. Synonym: dctp deaminase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus halodurans c-125. Organism_taxid: 272558. Gene: dcd, bh0368. Expressed in: bacillus halodurans c-125. Expression_system_taxid: 272558
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.35Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.209
|
R-free:
|
0.244
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Oehlenschlaeger,M.Loevgreen,M.Willemoes,P.Harris
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.B.Oehlenschlæger
et al.
(2015).
Bacillus halodurans Strain C125 Encodes and Synthesizes Enzymes from Both Known Pathways To Form dUMP Directly from Cytosine Deoxyribonucleotides.
Appl Environ Microbiol,
81,
3395-3404.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Jan-15
|
Release date:
|
18-Mar-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9KFV3
(DCDB_BACHD) -
dCTP deaminase, dUMP-forming from Halalkalibacterium halodurans (strain ATCC BAA-125 / DSM 18197 / FERM 7344 / JCM 9153 / C-125)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
177 a.a.
177 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.4.30
- dCTP deaminase (dUMP-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dCTP + 2 H2O = dUMP + NH4+ + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
dCTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 90.00% similarity
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
=
|
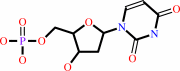 dUMP
dUMP
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Appl Environ Microbiol
81:3395-3404
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Bacillus halodurans Strain C125 Encodes and Synthesizes Enzymes from Both Known Pathways To Form dUMP Directly from Cytosine Deoxyribonucleotides.
|
|
C.B.Oehlenschlæger,
M.N.Løvgreen,
E.Reinauer,
E.Lehtinen,
M.L.Pind,
P.Harris,
J.Martinussen,
M.Willemoës.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Analysis of the genome of Bacillus halodurans strain C125 indicated that two
pathways leading from a cytosine deoxyribonucleotide to dUMP, used for dTMP
synthesis, were encoded by the genome of the bacterium. The genes that were
responsible, the comEB gene and the dcdB gene, encoding dCMP deaminase and the
bifunctional dCTP deaminase:dUTPase (DCD:DUT), respectively, were both shown to
be expressed in B. halodurans, and both genes were subject to repression by the
nucleosides thymidine and deoxycytidine. The latter nucleoside presumably exerts
its repression after deamination by cytidine deaminase. Both comEB and dcdB were
cloned, overexpressed in Escherichia coli, and purified to homogeneity. Both
enzymes were active and displayed the expected regulatory properties: activation
by dCTP for dCMP deaminase and dTTP inhibition for both enzymes. Structurally,
the B. halodurans enzyme resembled the Mycobacterium tuberculosis enzyme the
most. An investigation of sequenced genomes from other species of the genus
Bacillus revealed that not only the genome of B. halodurans but also the genomes
of Bacillus pseudofirmus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Bacillus hemicellulosilyticus,
Bacillus marmarensis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus megaterium encode both the
dCMP deaminase and the DCD:DUT enzymes. In addition, eight dcdB homologs from
Bacillus species within the genus for which the whole genome has not yet been
sequenced were registered in the NCBI Entrez database.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

