 |
PDBsum entry 3l6c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
X-ray crystal structure of rat serine racemase in complex with malonate a potent inhibitor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Serine racemase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Rattus norvegicus. Rat. Organism_taxid: 10116. Gene: srr. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.219
|
R-free:
|
0.267
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.A.Smith,V.Mack,A.Ebneth,I.Moraes,B.Felicetti,M.Wood,D.Schonfeld, O.Mather,A.Cesura,J.Barker
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.A.Smith
et al.
(2010).
The structure of mammalian serine racemase: evidence for conformational changes upon inhibitor binding.
J Biol Chem,
285,
12873-12881.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-Dec-09
|
Release date:
|
26-Jan-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q76EQ0
(SRR_RAT) -
Serine racemase from Rattus norvegicus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
333 a.a.
322 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.17
- L-serine ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-serine = pyruvate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-serine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 75.00% similarity
|
=
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate or iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
or
|
 iron-sulfur
iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.18
- D-serine ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-serine = pyruvate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
D-serine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 75.00% similarity
|
=
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.1.1.18
- serine racemase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-serine = D-serine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-serine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 75.00% similarity
|
=
|
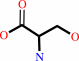 D-serine
D-serine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
285:12873-12881
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of mammalian serine racemase: evidence for conformational changes upon inhibitor binding.
|
|
M.A.Smith,
V.Mack,
A.Ebneth,
I.Moraes,
B.Felicetti,
M.Wood,
D.Schonfeld,
O.Mather,
A.Cesura,
J.Barker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Serine racemase is responsible for the synthesis of D-serine, an endogenous
co-agonist for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-type glutamate receptors (NMDARs).
This pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme is involved both in the reversible
conversion of L- to D-serine and serine catabolism by alpha,beta-elimination of
water, thereby regulating D-serine levels. Because D-serine affects NMDAR
signaling throughout the brain, serine racemase is a promising target for the
treatment of disorders related to NMDAR dysfunction. To provide a molecular
basis for rational drug design the x-ray crystal structures of human and rat
serine racemase were determined at 1.5- and 2.1-A resolution, respectively, and
in the presence and absence of the orthosteric inhibitor malonate. The
structures revealed a fold typical of beta-family pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
enzymes, with both a large domain and a flexible small domain associated into a
symmetric dimer, and indicated a ligand-induced rearrangement of the small
domain that organizes the active site for specific turnover of the substrate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

