 |
PDBsum entry 3e2s

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3e2s
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.88
- L-glutamate gamma-semialdehyde dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NAD+ + H2O = L-glutamate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
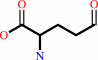 L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 88.89% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 76.36% similarity
|
=
|
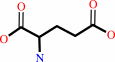 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.5.2
- proline dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-proline + a quinone = (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + a quinol + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
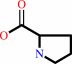 L-proline
L-proline
|
+
|
quinone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
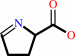 (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
(S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
|
+
|
quinol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:951-959
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A conserved active site tyrosine residue of proline dehydrogenase helps enforce the preference for proline over hydroxyproline as the substrate.
|
|
E.L.Ostrander,
J.D.Larson,
J.P.Schuermann,
J.J.Tanner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) catalyzes the oxidation of l-proline to
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate. PRODHs exhibit a pronounced preference for
proline over hydroxyproline (trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline) as the substrate, but
the basis for specificity is unknown. The goal of this study, therefore, is to
gain insight into the structural determinants of substrate specificity of this
class of enzyme, with a focus on understanding how PRODHs discriminate between
the two closely related molecules, proline and hydroxyproline. Two site-directed
mutants of the PRODH domain of Escherichia coli PutA were created: Y540A and
Y540S. Kinetics measurements were performed with both mutants. Crystal
structures of Y540S complexed with hydroxyproline, proline, and the proline
analogue l-tetrahydro-2-furoic acid were determined at resolutions of 1.75,
1.90, and 1.85 A, respectively. Mutation of Tyr540 increases the catalytic
efficiency for hydroxyproline 3-fold and decreases the specificity for proline
by factors of 20 (Y540S) and 50 (Y540A). The structures show that removal of the
large phenol side chain increases the volume of the substrate-binding pocket,
allowing sufficient room for the 4-hydroxyl of hydroxyproline. Furthermore, the
introduced serine residue participates in recognition of hydroxyproline by
forming a hydrogen bond with the 4-hydroxyl. This result has implications for
understanding the substrate specificity of the related enzyme human
hydroxyproline dehydrogenase, which has serine in place of tyrosine at this key
active site position. The kinetic and structural results suggest that Tyr540 is
an important determinant of specificity. Structurally, it serves as a negative
filter for hydroxyproline by clashing with the 4-hydroxyl group of this
potential substrate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Srivastava,
J.P.Schuermann,
T.A.White,
N.Krishnan,
N.Sanyal,
G.L.Hura,
A.Tan,
M.T.Henzl,
D.F.Becker,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2010).
Crystal structure of the bifunctional proline utilization A flavoenzyme from Bradyrhizobium japonicum.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
2878-2883.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

