 |
PDBsum entry 3c9t

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.4.16
- thiamine-phosphate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
thiamine phosphate + ATP = thiamine diphosphate + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
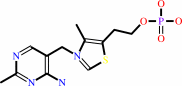 thiamine phosphate
thiamine phosphate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
thiamine diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:3810-3821
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural studies of thiamin monophosphate kinase in complex with substrates and products.
|
|
K.M.McCulloch,
C.Kinsland,
T.P.Begley,
S.E.Ealick.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Thiamin monophosphate kinase (ThiL) catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation
of thiamin monophosphate (TMP) to form thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP), the active
form of vitamin B 1. ThiL is a member of a small ATP binding superfamily that
also includes the purine biosynthetic enzymes, PurM and PurL, NiFe hydrogenase
maturation protein, HypE, and selenophosphate synthase, SelD. The latter four
enzymes are believed to utilize phosphorylated intermediates during catalysis.
To understand the mechanism of ThiL and its relationship to the other
superfamily members, we determined the structure of Aquifex aeolicus ThiL
(AaThiL) with nonhydrolyzable AMP-PCP and TMP, and also with the products of the
reaction, ADP and TPP. The results suggest that AaThiL utilizes a direct, inline
transfer of the gamma-phosphate of ATP to TMP rather than a phosphorylated
enzyme intermediate. The structure of ThiL is compared to those of PurM, PurL,
and HypE, and the ATP binding site is compared to that of PurL, for which
nucleotide complexes are available.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Gray,
and
J.C.Escalante-Semerena
(2010).
A new pathway for the synthesis of α-ribazole-phosphate in Listeria innocua.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
77,
1429-1438.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Challand,
F.T.Martins,
and
P.L.Roach
(2010).
Catalytic activity of the anaerobic tyrosine lyase required for thiamine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
5240-5248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Jurgenson,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2009).
The structural and biochemical foundations of thiamin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
78,
569-603.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
M.Morar,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Structural biology of the purine biosynthetic pathway.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
65,
3699-3724.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

