 |
PDBsum entry 3bul

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.13
- methionine synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Methionine Synthase
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + L-homocysteine = (6S)-5,6,7,8- tetrahydrofolate + L-methionine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
 L-homocysteine
L-homocysteine
|
=
|
(6S)-5,6,7,8- tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
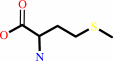 L-methionine
L-methionine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cob(II)alamin; Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cob(II)alamin
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
B12)
matches with 85.71% similarity
|
Zn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
105:4115-4120
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A disulfide-stabilized conformer of methionine synthase reveals an unexpected role for the histidine ligand of the cobalamin cofactor.
|
|
S.Datta,
M.Koutmos,
K.A.Pattridge,
M.L.Ludwig,
R.G.Matthews.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
B(12)-dependent methionine synthase (MetH) from Escherichia coli is a large
modular protein that is alternately methylated by methyltetrahydrofolate to form
methylcobalamin and demethylated by homocysteine to form cob(I)alamin. Major
domain rearrangements are required to allow cobalamin to react with three
different substrates: homocysteine, methyltetrahydrofolate, and
S-adenosyl-l-methionine (AdoMet). These same rearrangements appear to preclude
crystallization of the wild-type enzyme. Disulfide cross-linking was used to
lock a C-terminal fragment of the enzyme into a unique conformation. Cysteine
point mutations were introduced at Ile-690 and Gly-743. These cysteine residues
span the cap and the cobalamin-binding module and form a cross-link that reduces
the conformational space accessed by the enzyme, facilitating protein
crystallization. Here, we describe an x-ray structure of the mutant fragment in
the reactivation conformation; this conformation enables the transfer of a
methyl group from AdoMet to the cobalamin cofactor. In the structure, the axial
ligand to the cobalamin, His-759, dissociates from the cobalamin and forms
intermodular contacts with residues in the AdoMet-binding module. This
unanticipated intermodular interaction is expected to play a major role in
controlling the distribution of conformers required for the catalytic and the
reactivation cycles of the enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
The catalytic (red) and reactivation (blue) cycles of E. coli
MetH. During catalysis the cobalamin cofactor is alternately
methylated by CH[3]-H[4]folate and demethylated by Hcy. The
cob(I)alamin form of the enzyme is occasionally oxidized to form
the inactive cob(II)alamin form. Return of this species to the
catalytic cycle involves reduction with electrons derived from
reduced flavodoxin and methylation with a methyl group derived
from AdoMet.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Intermodular interactions involving His-759 in the His-off
state. Nε2 of His-759 interacts with the AdoMet module directly
through a hydrogen bond to Asp-1093 and via a water-mediated
hydrogen bond to Glu-1069. Nδ1 of His-759 forms a hydrogen bond
with the amide of the propionamide side chain of ring B of the
cobalamin (data not shown).
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kung,
N.Ando,
T.I.Doukov,
L.C.Blasiak,
G.Bender,
J.Seravalli,
S.W.Ragsdale,
and
C.L.Drennan
(2012).
Visualizing molecular juggling within a B12-dependent methyltransferase complex.
|
| |
Nature,
484,
265-269.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhu,
X.Gu,
S.Zhang,
Y.Liu,
Z.X.Huang,
and
X.Tan
(2011).
Efficient expression and purification of methyltransferase in acetyl-coenzyme a synthesis pathway of the human pathogen Clostridium Difficile.
|
| |
Protein Expr Purif,
78,
86-93.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Koutmos,
S.Datta,
K.A.Pattridge,
J.L.Smith,
and
R.G.Matthews
(2009).
Insights into the reactivation of cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
18527-18532.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.G.Matthews
(2009).
A love affair with vitamins.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
26217-26228.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.G.Matthews,
M.Koutmos,
and
S.Datta
(2008).
Cobalamin-dependent and cobamide-dependent methyltransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
18,
658-666.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

