 |
PDBsum entry 2yr4

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2yr4
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.13.12.9
- phenylalanine 2-monooxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-phenylalanine + O2 = 2-phenylacetamide + CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
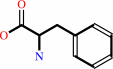 L-phenylalanine
L-phenylalanine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
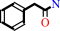 2-phenylacetamide
2-phenylacetamide
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
283:16584-16590
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of proteolytic activation of L-phenylalanine oxidase from Pseudomonas sp. P-501.
|
|
K.Ida,
M.Kurabayashi,
M.Suguro,
Y.Hiruma,
T.Hikima,
M.Yamomoto,
H.Suzuki.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The mature form of l-phenylalanine oxidase (PAOpt) from Pseudomonas sp. P-501
was generated and activated by the proteolytic cleavage of a noncatalytic
proenzyme (proPAO). The crystal structures of proPAO, PAOpt, and the
PAOpt-o-amino benzoate (AB) complex were determined at 1.7, 1.25, and 1.35A
resolutions, respectively. The structure of proPAO suggests that the prosequence
peptide of proPAO occupies the funnel (pathway) of the substrate amino acid from
the outside of the protein to the interior flavin ring, whereas the funnel is
closed with the hydrophobic residues at its vestibule in both PAOpt and the
PAOpt-AB complex. All three structures have an oxygen channel that is open to
the surface of the protein from the flavin ring. These results suggest that
structural changes were induced by proteolysis; that is, the proteolysis of
proPAO removes the prosequence and closes the funnel to keep the active site
hydrophobic but keeps the oxygen channel open. The possibility that an
interaction of the hydrophobic side chain of substrate with the residues of the
vestibule region may open the funnel as a putative amino acid channel is
discussed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

