 |
PDBsum entry 2wb2

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.99.3
- deoxyribodipyrimidine photo-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
EC 4.1.99.3
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
cyclobutadipyrimidine (in DNA) = 2 pyrimidine residues (in DNA)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
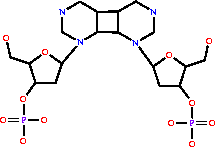 cyclobutadipyrimidine (in DNA)
cyclobutadipyrimidine (in DNA)
|
=
|
2
×
pyrimidine residues (in DNA)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate; FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
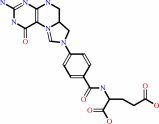 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate
5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate
|
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chemistry
15:10387-10396
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the T(6-4)C lesion in complex with a (6-4) DNA photolyase and repair of UV-induced (6-4) and Dewar photolesions.
|
|
A.F.Glas,
S.Schneider,
M.J.Maul,
U.Hennecke,
T.Carell.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
UV-light irradiation induces the formation of highly mutagenic lesions in DNA,
such as cis-syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD photoproducts),
pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts ((6-4) photoproducts) and their Dewar
valence isomers ((Dew) photoproducts). Here we describe the synthesis of defined
DNA strands containing these lesions by direct irradiation. We show that all
lesions are efficiently repaired except for the T(Dew)T lesion, which cannot be
cleaved by the repair enzyme under our conditions. A crystal structure of a
T(6-4)C lesion containing DNA duplex in complex with the (6-4) photolyase from
Drosophila melanogaster provides insight into the molecular recognition event of
a cytosine derived photolesion for the first time. In light of the previously
postulated repair mechanism, which involves rearrangement of the (6-4) lesions
into strained four-membered ring repair intermediates, it is surprising that the
not rearranged T(6-4)C lesion is observed in the active site. The structure,
therefore, provides additional support for the newly postulated repair mechanism
that avoids this rearrangement step and argues for a direct electron injection
into the lesion as the first step of the repair reaction performed by (6-4) DNA
photolyases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Li,
Z.Liu,
C.Tan,
X.Guo,
L.Wang,
A.Sancar,
and
D.Zhong
(2010).
Dynamics and mechanism of repair of ultraviolet-induced (6-4) photoproduct by photolyase.
|
| |
Nature,
466,
887-890.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

