 |
PDBsum entry 2vfs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2vfs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.3.41
- alditol oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an alditol + O2 = an aldose + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
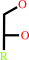 alditol
alditol
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
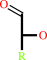 aldose
aldose
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:978-985
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural analysis of the catalytic mechanism and stereoselectivity in Streptomyces coelicolor alditol oxidase.
|
|
F.Forneris,
D.P.Heuts,
M.Delvecchio,
S.Rovida,
M.W.Fraaije,
A.Mattevi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Alditol oxidase (AldO) from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) is a soluble monomeric
flavin-dependent oxidase that performs selective oxidation of the terminal
primary hydroxyl group of several alditols. Here, we report the crystal
structure of the recombinant enzyme in its native state and in complex with both
six-carbon (mannitol and sorbitol) and five-carbon substrates (xylitol). AldO
shares the same folding topology of the members of the vanillyl-alcohol oxidase
family of flavoenzymes and exhibits a covalently linked FAD which is located at
the bottom of a funnel-shaped pocket that forms the active site. The high
resolution of the three-dimensional structures highlights a well-defined
hydrogen-bonding network that tightly constrains the substrate in the productive
conformation for catalysis. Substrate binding occurs through a lock-and-key
mechanism and does not induce conformational changes with respect to the
ligand-free protein. A network of charged residues is proposed to favor
catalysis through stabilization of the deprotonated form of the substrate. A His
side chain acts as back door that "pushes" the substrate-reactive carbon atom
toward the N5-C4a locus of the flavin. Analysis of the three-dimensional
structure reveals possible pathways for diffusion of molecular oxygen and a
small cavity on the re side of the flavin that may host oxygen during FAD
reoxidation. These features combined with the tight shape of the catalytic site
provide insights into the mechanism of AldO-mediated regioselective oxidation
reactions and its substrate specificity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Rosini,
G.Molla,
S.Ghisla,
and
L.Pollegioni
(2011).
On the reaction of D-amino acid oxidase with dioxygen: O2 diffusion pathways and enhancement of reactivity.
|
| |
FEBS J,
278,
482-492.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kachalova,
K.Decker,
A.Holt,
and
H.D.Bartunik
(2011).
Crystallographic snapshots of the complete reaction cycle of nicotine degradation by an amine oxidase of the monoamine oxidase (MAO) family.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
4800-4805.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.W.Han,
C.Bakolitsa,
M.D.Miller,
A.Kumar,
D.Carlton,
R.J.Najmanovich,
P.Abdubek,
T.Astakhova,
H.L.Axelrod,
C.Chen,
H.J.Chiu,
T.Clayton,
D.Das,
M.C.Deller,
L.Duan,
D.Ernst,
J.Feuerhelm,
J.C.Grant,
A.Grzechnik,
L.Jaroszewski,
K.K.Jin,
H.A.Johnson,
H.E.Klock,
M.W.Knuth,
P.Kozbial,
S.S.Krishna,
D.Marciano,
D.McMullan,
A.T.Morse,
E.Nigoghossian,
L.Okach,
R.Reyes,
C.L.Rife,
N.Sefcovic,
H.J.Tien,
C.B.Trame,
H.van den Bedem,
D.Weekes,
Q.Xu,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.M.Deacon,
A.Godzik,
S.A.Lesley,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2010).
Structures of the first representatives of Pfam family PF06938 (DUF1285) reveal a new fold with repeated structural motifs and possible involvement in signal transduction.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
66,
1218-1225.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Heuts,
N.S.Scrutton,
W.S.McIntire,
and
M.W.Fraaije
(2009).
What's in a covalent bond? On the role and formation of covalently bound flavin cofactors.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
3405-3427.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.van Bloois,
R.T.Winter,
D.B.Janssen,
and
M.W.Fraaije
(2009).
Export of functional Streptomyces coelicolor alditol oxidase to the periplasm or cell surface of Escherichia coli and its application in whole-cell biocatalysis.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
83,
679-687.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.G.Leferink,
M.W.Fraaije,
H.J.Joosten,
P.J.Schaap,
A.Mattevi,
and
W.J.van Berkel
(2009).
Identification of a gatekeeper residue that prevents dehydrogenases from acting as oxidases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
4392-4397.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Baron,
C.Riley,
P.Chenprakhon,
K.Thotsaporn,
R.T.Winter,
A.Alfieri,
F.Forneris,
W.J.van Berkel,
P.Chaiyen,
M.W.Fraaije,
A.Mattevi,
and
J.A.McCammon
(2009).
Multiple pathways guide oxygen diffusion into flavoenzyme active sites.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
10603-10608.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
R.C.Bruckner,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2008).
Identification of the oxygen activation site in monomeric sarcosine oxidase: role of Lys265 in catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
9124-9135.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

