 |
PDBsum entry 2pan

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of e. Coli glyoxylate carboligase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glyoxylate carboligase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: tartronate-semialdehyde synthase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Strain: xl1. Gene: gcl. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.220
|
R-free:
|
0.253
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Kaplun,D.M.Chipman,Z.Barak,M.Vyazmensky,B.Shaanan
|
Key ref:

|
 |
A.Kaplun
et al.
(2008).
Glyoxylate carboligase lacks the canonical active site glutamate of thiamine-dependent enzymes.
Nat Chem Biol,
4,
113-118.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Mar-07
|
Release date:
|
01-Jan-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0AEP7
(GCL_ECOLI) -
Glyoxylate carboligase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
593 a.a.
592 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.47
- tartronate-semialdehyde synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 glyoxylate + H+ = 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
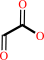 2
×
glyoxylate
2
×
glyoxylate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
=
|
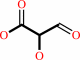 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate
2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
TPP)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Chem Biol
4:113-118
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Glyoxylate carboligase lacks the canonical active site glutamate of thiamine-dependent enzymes.
|
|
A.Kaplun,
E.Binshtein,
M.Vyazmensky,
A.Steinmetz,
Z.Barak,
D.M.Chipman,
K.Tittmann,
B.Shaanan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Thiamine diphosphate (ThDP), a derivative of vitamin B1, is an enzymatic
cofactor whose special chemical properties allow it to play critical mechanistic
roles in a number of essential metabolic enzymes. It has been assumed that all
ThDP-dependent enzymes exploit a polar interaction between a strictly conserved
glutamate and the N1' of the ThDP moiety. The crystal structure of glyoxylate
carboligase challenges this paradigm by revealing that valine replaces the
conserved glutamate. Through kinetic, spectroscopic and site-directed
mutagenesis studies, we show that although this extreme change lowers the rate
of the initial step of the enzymatic reaction, it ensures efficient progress
through subsequent steps. Glyoxylate carboligase thus provides a unique
illustration of the fine tuning between catalytic stages imposed during
evolution on enzymes catalyzing multistep processes.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
(a) Conserved glutamate residue in other ThDP-dependent
enzymes interacts with N1' of bound ThDP. Shown are the
glutamate and ThDP after superposition of pyruvate oxidase (PDB
code 1POX, green), pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDB code 1NI4, gray),
transketolase (PDB code 1TRK, magenta) and pyruvate
decarboxylase (PDB code 1PVD, yellow). ThDP adopts the typical
V-shaped conformation juxtaposing the 4'-amino group and the
reactive C2. (b) The conserved glutamate participates in the
aminopyrimidine-iminopyrimidine tautomerization of ThDP. The
iminopyrimidine acts as the general base that removes the proton
from C2 of the thiazol moiety. (c) The reaction catalyzed by GCL.
|
 |
Figure 2.
(a) Structure of GCL protomer (ribbons) with cofactors
(stick). The three domains are the PYR domain (residues 1–185,
magenta), contacting the ThDP aminopyrimidine group; the FAD
domain (residues 186–357, blue), surrounding the FAD group;
and the PP domain (residues 358–592, yellow), providing polar
interactions with the ThDP diphosphate moiety. (b) Electron
density around Val51 and ThDP. 2F[o] – F[c]  [a]-weighted,
contoured at 1 [a]-weighted,
contoured at 1  level
around Val51 (magenta) and neighboring residues. (c) Similarity
between the loop containing Val51 in GCL and other
ThDP-dependent enzymes. GCL and seven other enzymes with top Z
similarity scores according to the Dali^42 server were
superimposed.
(d) Hydrophobic environment of the thiazol in GCL: Residues are colored
according a hydrophobicity scale (aquamarine - hydrophilic, gold -
hydrophobic). Hydrophobic residues in contact with the thiazol and
pyrimidine of ThDP are depicted as space-filling models. Note that the
thiazol is sandwiched between those residues. The labels of residues
contributed by the neighboring subunit are in pink. level
around Val51 (magenta) and neighboring residues. (c) Similarity
between the loop containing Val51 in GCL and other
ThDP-dependent enzymes. GCL and seven other enzymes with top Z
similarity scores according to the Dali^42 server were
superimposed.
(d) Hydrophobic environment of the thiazol in GCL: Residues are colored
according a hydrophobicity scale (aquamarine - hydrophilic, gold -
hydrophobic). Hydrophobic residues in contact with the thiazol and
pyrimidine of ThDP are depicted as space-filling models. Note that the
thiazol is sandwiched between those residues. The labels of residues
contributed by the neighboring subunit are in pink.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Chem Biol
(2008,
4,
113-118)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
T.Werther,
A.Zimmer,
G.Wille,
R.Golbik,
M.S.Weiss,
and
S.König
(2010).
New insights into structure-function relationships of oxalyl CoA decarboxylase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
2628-2640.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Shaanan,
and
D.M.Chipman
(2009).
Reaction mechanisms of thiamin diphosphate enzymes: new insights into the role of a conserved glutamate residue.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
2447-2453.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Tittmann
(2009).
Reaction mechanisms of thiamin diphosphate enzymes: redox reactions.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
2454-2468.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.S.Nemeria,
S.Chakraborty,
A.Balakrishnan,
and
F.Jordan
(2009).
Reaction mechanisms of thiamin diphosphate enzymes: defining states of ionization and tautomerization of the cofactor at individual steps.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
2432-3446.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Neumann,
A.Weidner,
A.Pech,
M.T.Stubbs,
and
K.Tittmann
(2008).
Structural basis for membrane binding and catalytic activation of the peripheral membrane enzyme pyruvate oxidase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
17390-17395.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

