 |
PDBsum entry 2o2k

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the activation domain of human methionine synthase isoform/mutant d963e/k1071n
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Methionine synthase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: enzyme domain, residues 926-1265. Synonym: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate--homocysteine methyltransferase, methionine synthase, vitamin-b12 dependent, ms. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: mtr. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.211
|
R-free:
|
0.248
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.R.Wolthers,H.S.Toogood,T.A.Jowitt,K.R.Marshall,D.Leys,N.S.Scrutton
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.R.Wolthers
et al.
(2007).
Crystal structure and solution characterization of the activation domain of human methionine synthase.
Febs J,
274,
738-750.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
30-Nov-06
|
Release date:
|
19-Dec-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q99707
(METH_HUMAN) -
Methionine synthase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1265 a.a.
332 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.13
- methionine synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Methionine Synthase
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + L-homocysteine = (6S)-5,6,7,8- tetrahydrofolate + L-methionine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
 L-homocysteine
L-homocysteine
|
=
|
(6S)-5,6,7,8- tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
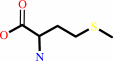 L-methionine
L-methionine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cob(II)alamin; Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
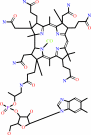 Cob(II)alamin
Cob(II)alamin
|
Zn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Febs J
274:738-750
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure and solution characterization of the activation domain of human methionine synthase.
|
|
K.R.Wolthers,
H.S.Toogood,
T.A.Jowitt,
K.R.Marshall,
D.Leys,
N.S.Scrutton.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Human methionine synthase (hMS) is a multidomain cobalamin-dependent enzyme that
catalyses the conversion of homocysteine to methionine by methyl group transfer.
We report here the 1.6 A crystal structure of the C-terminal activation domain
of hMS. The structure is C-shaped with the core comprising mixed alpha and beta
regions, dominated by a twisted antiparallel beta sheet with a beta-meander
region. These features, including the positions of the active-site residues, are
similar to the activation domain of Escherichia coli cobalamin-dependent MS
(MetH). Structural and solution studies suggest a small proportion of hMS
activation domain exists in a dimeric form, which contrasts with the monomeric
form of the E. coli homologue. Fluorescence studies show that human activation
domain interacts with the FMN-binding domain of human methionine synthase
reductase (hMSR). This interaction is enhanced in the presence of
S-adenosyl-methionine. Binding of the D963E/K1071N mutant activation domain to
the FMN domain of MSR is weaker than with wild-type activation domain. This
suggests that one or both of the residues D963 and K1071 are important in
partner binding. Key differences in the sequences and structures of hMS and MetH
activation domains are recognized and include a major reorientation of an
extended 3(10)-containing loop in the human protein. This structural alteration
might reflect differences in their respective reactivation complexes and/or
potential for dimer formation. The reported structure is a component of the
multidomain hMS : MSR complex, and represents an important step in understanding
the impact of clinical mutations and polymorphisms in this key electron transfer
complex.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Rigby,
X.Lou,
H.S.Toogood,
K.R.Wolthers,
and
N.S.Scrutton
(2011).
ELDOR spectroscopy reveals that energy landscapes in human methionine synthase reductase are extensively remodelled following ligand and partner protein binding.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
863-867.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.R.Wolthers,
and
N.S.Scrutton
(2009).
Cobalamin uptake and reactivation occurs through specific protein interactions in the methionine synthase-methionine synthase reductase complex.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
1942-1951.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.G.Matthews,
M.Koutmos,
and
S.Datta
(2008).
Cobalamin-dependent and cobamide-dependent methyltransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
18,
658-666.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

