 |
PDBsum entry 2nxg

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural and mechanistic changes along an engineered path from metallo to non-metallo kdo8p synthase.
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphooctonate aldolase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxyoctonate aldolase, 3-deoxy-d- manno-octulosonic acid 8- phosphate synthetase, kdo-8-phosphate synthetase, kdo 8-p synthase, kdops. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Aquifex aeolicus. Organism_taxid: 63363. Gene: kdsa. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.95Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.209
|
R-free:
|
0.243
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.Kona,X.Xu,P.Martin,P.Kuzmic,D.L.Gatti
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
F.Kona
et al.
(2007).
Structural and mechanistic changes along an engineered path from metallo to nonmetallo 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate 8-phosphate synthases.
Biochemistry,
46,
4532-4544.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Nov-06
|
Release date:
|
24-Apr-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O66496
(KDSA_AQUAE) -
2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphooctonate aldolase from Aquifex aeolicus (strain VF5)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
267 a.a.
263 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.55
- 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-arabinose 5-phosphate + phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O = 3-deoxy-alpha-D- manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
D-arabinose 5-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
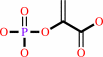 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
3-deoxy-alpha-D- manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
46:4532-4544
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and mechanistic changes along an engineered path from metallo to nonmetallo 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate 8-phosphate synthases.
|
|
F.Kona,
X.Xu,
P.Martin,
P.Kuzmic,
D.L.Gatti.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
There are two classes of KDO8P synthases characterized respectively by the
presence or absence of a metal in the active site. The nonmetallo KDO8PS from
Escherichia coli and the metallo KDO8PS from Aquifex aeolicus are the best
characterized members of each class. All amino acid residues that make important
contacts with the substrates are conserved in both enzymes with the exception of
Pro-10, Cys-11, Ser-235, and Gln-237 of the A. aeolicus enzyme, which correspond
respectively to Met-25, Asn-26, Pro-252, and Ala-254 in the E. coli enzyme.
Interconversion between the two forms of KDO8P synthases can be achieved by
substituting the metal-coordinating cysteine of metallo synthases with the
corresponding asparagine of nonmetallo synthases, and vice versa. In this report
we describe the structural changes elicited by the C11N mutation and by three
combinations of mutations (P10M/C11N, C11N/S235P/Q237A, and
P10M/C11N/S235P/Q237A) situated along possible evolutionary paths connecting the
A. aeolicus and the E. coli enzyme. All four mutants are not capable of binding
metal and lack the structural asymmetry among subunits with regard to substrate
binding and conformation of the L7 loop, which is typical of A. aeolicus
wild-type KDO8PS but is absent in the E. coli enzyme. Despite the lack of the
active site metal, the mutant enzymes display levels of activity ranging from
46% to 24% of the wild type. With the sole exception of the quadruple mutant,
metal loss does not affect the thermal stability of KDO8PS. The free energy of
unfolding in water is also either unchanged or even increased in the mutant
enzymes, suggesting that the primary role of the active site metal in A.
aeolicus KDO8PS is not to increase the enzyme stability. In all four mutants A5P
binding displaces a water molecule located on the si side of PEP. In particular,
in the double and triple mutant, A5P binds with the aldehyde carbonyl in
hydrogen bond distance of Asn-11, while in the wild type this functional group
points away from Cys-11. This alternative conformation of A5P is likely to have
functional significance as it resembles the conformation of the acyclic reaction
intermediate, which is observed here for the first time in some of the active
sites of the triple mutant. The direct visualization of this intermediate by
X-ray crystallography confirms earlier mechanistic models of KDO8P synthesis. In
particular, the configuration of the C2 chiral center of the intermediate
supports a model of the reaction in nonmetallo KDO8PS, in which water attacks an
oxocarbenium ion or PEP from the si side of C2. Several explanations are offered
to reconcile this observation with the fact that no water molecule is observed
at this position in the mutant enzymes in the presence of both PEP and A5P.
Significant differences were observed between the wild-type and the mutant
enzymes in the Km values for PEP and A5P and in the Kd values for inorganic
phosphate and R5P. These differences may reflect an evolutionary adaptation of
metallo and nonmetallo KDO8PS's to the cellular concentrations of these
metabolites in their respective hosts.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Roberts,
C.Furdui,
and
K.S.Anderson
(2010).
Observation of a chemically labile, noncovalent enzyme intermediate in the reaction of metal-dependent Aquifex pyrophilus KDO8PS by time-resolved mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,
24,
1919-1924.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Tumbale,
and
K.Brew
(2009).
Characterization of a metal-independent CAZy family 6 glycosyltransferase from Bacteroides ovatus.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
25126-25134.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

