 |
PDBsum entry 2ii4

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of a cubic core of the dihydrolipoamide acyltransferase (e2b) component in the branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (bckdc), coenzyme a-bound form
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Lipoamide acyltransferase component of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Fragment: core (catalytic) domain. Synonym: dihydrolipoyllysine-residue (2-methylpropanoyl)transferase, e2, dihydrolipoamide branched chain transacylase, bckad e2 subunit. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Cattle. Organism_taxid: 9913. Gene: dbt. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.59Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.173
|
R-free:
|
0.229
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Kato,R.M.Wynn,J.L.Chuang,C.A.Brautigam,M.Custorio,D.T.Chuang
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.Kato
et al.
(2006).
A synchronized substrate-gating mechanism revealed by cubic-core structure of the bovine branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex.
EMBO J,
25,
5983-5994.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Sep-06
|
Release date:
|
26-Dec-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P11181
(ODB2_BOVIN) -
Lipoamide acyltransferase component of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
482 a.a.
234 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.168
- dihydrolipoyllysine-residue (2-methylpropanoyl)transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Oxo-acid dehydrogenase complexes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-[(R)-dihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein] + 2-methylpropanoyl-CoA = N6-[(R)-S(8)-2-methylpropanoyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein] + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-[(R)-dihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
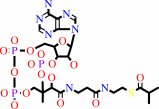 2-methylpropanoyl-CoA
2-methylpropanoyl-CoA
|
=
|
N(6)-[(R)-S(8)-2-methylpropanoyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
EMBO J
25:5983-5994
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A synchronized substrate-gating mechanism revealed by cubic-core structure of the bovine branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex.
|
|
M.Kato,
R.M.Wynn,
J.L.Chuang,
C.A.Brautigam,
M.Custorio,
D.T.Chuang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The dihydrolipoamide acyltransferase (E2b) component of the branched-chain
alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex forms a cubic scaffold that catalyzes
acyltransfer from S-acyldihydrolipoamide to CoA to produce acyl-CoA. We have
determined the first crystal structures of a mammalian (bovine) E2b core domain
with and without a bound CoA or acyl-CoA. These structures reveal both
hydrophobic and the previously unreported ionic interactions between
two-fold-related trimers that build up the cubic core. The entrance of the
dihydrolipoamide-binding site in a 30-A long active-site channel is closed in
the apo and acyl-CoA-bound structures. CoA binding to one entrance of the
channel promotes a conformational change in the channel, resulting in the
opening of the opposite dihydrolipoamide gate. Binding experiments show that the
affinity of the E2b core for dihydrolipoamide is markedly increased in the
presence of CoA. The result buttresses the model that CoA binding is responsible
for the opening of the dihydrolipoamide gate. We suggest that this gating
mechanism synchronizes the binding of the two substrates to the active-site
channel, which serves as a feed-forward switch to coordinate the E2b-catalyzed
acyltransfer reaction.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4 A CoA-mediated gating mechanism for synchronized
dihydrolipoamide binding in the active-site channel of bovine
E2bCD. (A) Stereo view of the CoA-binding site of E2bCD-CoA
(short soak). The bound CoA in the 'in' conformation and its
surrounding residues are shown in stick models. Residues from
the three-fold-related subunit are shown in cyan. The residues
in magenta are the gatekeepers at the dihydrolipoamide entrance
of the active-site channel. Water molecules are shown as small
spheres. The 2F[o]-F[c] density of the bound CoA is superimposed
at a 1-  contour
level. (B) The bound IB-CoA in the 'out' conformation in
E2bCD-IB-CoA. The 2F[o]-F[c] densities are at the 1- contour
level. (B) The bound IB-CoA in the 'out' conformation in
E2bCD-IB-CoA. The 2F[o]-F[c] densities are at the 1-  level.
(C) The oxidized CoA in the 'in' conformation in E2bCD-CoA (long
soak). Three of the eight E2bCD monomers in the asymmetric unit
of this crystal show this structure. The omit density of the
oxidized CoA was at the 1- level.
(C) The oxidized CoA in the 'in' conformation in E2bCD-CoA (long
soak). Three of the eight E2bCD monomers in the asymmetric unit
of this crystal show this structure. The omit density of the
oxidized CoA was at the 1-  level.
(D) The disordered pantetheine tail of the CoA (the 'out'
conformation) bound to the remaining five monomers in E2bCD-CoA
(long soak). The 2F[o]-F[c] density is contoured at the 1- level.
(D) The disordered pantetheine tail of the CoA (the 'out'
conformation) bound to the remaining five monomers in E2bCD-CoA
(long soak). The 2F[o]-F[c] density is contoured at the 1-  level.
(E) Superimposed gating turns and bound cofactors; white: apo,
green: E2bCD-CoA (short soak), orange: E2bCD-IB-CoA. The bound
CoA (carbon atoms in green) in E2bCD-CoA (short soak) is in the
'in' conformation, whereas the pantetheine tail of the bound
IB-CoA (carbons in orange) in E2bCD-IB-CoA is disordered (the
'out' conformation). The gray arrow indicates the direction of
the dihydrolipoamide-binding site. The gatekeeper residues are
in magenta. (F) Surface model of the closed dihydrolipoamide
gate in the apo E2bCD structure. Three gatekeeper residues
(Leu293, Val295 and Leu353) are colored in magenta and the
gating turn in red. (G) The open gate for the
dihydrolipoamide-binding site in E2bCD-CoA (short soak). The
thiol group of the bound CoA in the 'in' conformation is shown
in yellow. (H) The closed dihydrolipoamide gate in E2bCD-IB-CoA. level.
(E) Superimposed gating turns and bound cofactors; white: apo,
green: E2bCD-CoA (short soak), orange: E2bCD-IB-CoA. The bound
CoA (carbon atoms in green) in E2bCD-CoA (short soak) is in the
'in' conformation, whereas the pantetheine tail of the bound
IB-CoA (carbons in orange) in E2bCD-IB-CoA is disordered (the
'out' conformation). The gray arrow indicates the direction of
the dihydrolipoamide-binding site. The gatekeeper residues are
in magenta. (F) Surface model of the closed dihydrolipoamide
gate in the apo E2bCD structure. Three gatekeeper residues
(Leu293, Val295 and Leu353) are colored in magenta and the
gating turn in red. (G) The open gate for the
dihydrolipoamide-binding site in E2bCD-CoA (short soak). The
thiol group of the bound CoA in the 'in' conformation is shown
in yellow. (H) The closed dihydrolipoamide gate in E2bCD-IB-CoA.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5 The proposed scheme for the bovine E2bCD-catalyzed
acyltransfer reaction cycle. The active-site channel of bovine
E2bCD is depicted with the CoA-binding site on the left side and
the dihydrolipoamide-binding site on the right. The catalytic
resides in the channel (His391' and Ser338) and two important
residues on the gating turn (Leu293 and Asp288) are shown. Gray
dotted lines: H-bonds, a green oval with 'Ac': acyl group,
yellow dots: thiol groups and red dots: water molecules. See the
text for details of each reaction step.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
EMBO J
(2006,
25,
5983-5994)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.Brunetti-Pierri,
B.Lanpher,
A.Erez,
E.A.Ananieva,
M.Islam,
J.C.Marini,
Q.Sun,
C.Yu,
M.Hegde,
J.Li,
R.M.Wynn,
D.T.Chuang,
S.Hutson,
and
B.Lee
(2011).
Phenylbutyrate therapy for maple syrup urine disease.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
20,
631-640.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Yu,
Y.Hiromasa,
H.Tsen,
J.K.Stoops,
T.E.Roche,
and
Z.H.Zhou
(2008).
Structures of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex cores: a highly conserved catalytic center with flexible N-terminal domains.
|
| |
Structure,
16,
104-114.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Islam,
R.Wallin,
R.M.Wynn,
M.Conway,
H.Fujii,
J.A.Mobley,
D.T.Chuang,
and
S.M.Hutson
(2007).
A novel branched-chain amino acid metabolon. Protein-protein interactions in a supramolecular complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
11893-11903.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

