 |
PDBsum entry 2fje

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2fje
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, C, B, D:
E.C.1.8.99.2
- adenylyl-sulfate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
sulfite + A + AMP + 2 H+ = adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate + AH2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
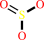 sulfite
sulfite
|
+
|
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
=
|
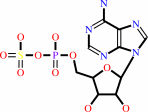 adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate
adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate
|
+
|
AH2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
Fe cation
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
45:2960-2967
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Reaction mechanism of the iron-sulfur flavoenzyme adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate reductase based on the structural characterization of different enzymatic states.
|
|
A.Schiffer,
G.Fritz,
P.M.Kroneck,
U.Ermler.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The iron-sulfur flavoenzyme adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (APS) reductase
catalyzes a key reaction of the global sulfur cycle by reversibly transforming
APS to sulfite and AMP. The structures of the dissimilatory enzyme from
Archaeoglobus fulgidus in the reduced state (FAD(red)) and in the sulfite adduct
state (FAD-sulfite-AMP) have been recently elucidated at 1.6 and 2.5 A
resolution, respectively. Here we present new structural features of the enzyme
trapped in four different catalytically relevant states that provide us with a
detailed picture of its reaction cycle. In the oxidized state (FAD(ox)), the
isoalloxazine moiety of the FAD cofactor exhibits a similarly bent conformation
as observed in the structure of the reduced enzyme. In the APS-bound state
(FAD(ox)-APS), the substrate APS is embedded into a 17 A long substrate channel
in such a way that the isoalloxazine ring is pushed toward the channel bottom,
thereby producing a compressed enzyme-substrate complex. A clamp formed by
residues ArgA317 and LeuA278 to fix the adenine ring and the curved APS
conformation appear to be key factors to hold APS in a strained conformation.
This energy-rich state is relaxed during the attack of APS on the reduced FAD. A
relaxed FAD-sulfite adduct is observed in the structure of the FAD-sulfite
state. Finally, a FAD-sulfite-AMP1 state with AMP within van der Waals distance
of the sulfite adduct could be characterized. This structure documents how
adjacent negative charges are stabilized by the protein matrix which is crucial
for forming APS from AMP and sulfite in the reverse reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Y.L.Chiang,
Y.C.Hsieh,
J.Y.Fang,
E.H.Liu,
Y.C.Huang,
P.Chuankhayan,
J.Jeyakanthan,
M.Y.Liu,
S.I.Chan,
and
C.J.Chen
(2009).
Crystal structure of Adenylylsulfate reductase from Desulfovibrio gigas suggests a potential self-regulation mechanism involving the C terminus of the beta-subunit.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
7597-7608.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Meyer,
and
J.Kuever
(2008).
Homology Modeling of Dissimilatory APS Reductases (AprBA) of Sulfur-Oxidizing and Sulfate-Reducing Prokaryotes.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
3,
e1514.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ogata,
A.Goenka Agrawal,
A.P.Kaur,
R.Goddard,
W.Gärtner,
and
W.Lubitz
(2008).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of adenylylsulfate reductase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris Miyazaki F.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
1010-1012.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.G.Leferink,
W.A.van den Berg,
and
W.J.van Berkel
(2008).
l-Galactono-gamma-lactone dehydrogenase from Arabidopsis thaliana, a flavoprotein involved in vitamin C biosynthesis.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
713-726.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Sato,
H.Atomi,
and
T.Imanaka
(2007).
Archaeal type III RuBisCOs function in a pathway for AMP metabolism.
|
| |
Science,
315,
1003-1006.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.De Colibus,
and
A.Mattevi
(2006).
New frontiers in structural flavoenzymology.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
16,
722-728.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

