 |
PDBsum entry 2de4

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.13.1.3
- 2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate desulfinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate + H2O = biphenyl-2-ol + sulfite + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
biphenyl-2-ol
|
+
|
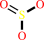 sulfite
sulfite
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
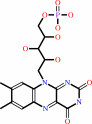 FMN
FMN
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:32534-32539
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure and desulfurization mechanism of 2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinic acid desulfinase.
|
|
W.C.Lee,
T.Ohshiro,
T.Matsubara,
Y.Izumi,
M.Tanokura.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The desulfurization of dibenzothiophene in Rhodococcus erythropolis is catalyzed
by two monooxygenases, DszA and DszC, and a desulfinase, DszB. In the last step
of this pathway, DszB hydrolyzes 2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinic acid into
2-hydroxybiphenyl and sulfite. We report on the crystal structures of DszB and
an inactive mutant of DszB in complex with substrates at resolutions of 1.8A or
better. The overall fold of DszB is similar to those of periplasmic
substrate-binding proteins. In the substrate complexes, biphenyl rings of
substrates are recognized by extensive hydrophobic interactions with the active
site residues. Binding of substrates accompanies structural changes of the
active site loops and recruits His(60) to the active site. The sulfinate group
of bound substrates forms hydrogen bonds with side chains of Ser(27), His(60),
and Arg(70), each of which is shown by site-directed mutagenesis to be essential
for the activity. In our proposed reaction mechanism, Cys(27) functions as a
nucleophile and seems to be activated by the sulfinate group of substrates,
whereas His(60) and Arg(70) orient the syn orbital of sulfinate oxygen to the
sulfhydryl hydrogen of Cys(27) and stabilize the negatively charged reaction
intermediate. Cys, His, and Arg residues are conserved in putative proteins
homologous to DszB, which are presumed to constitute a new family of
desulfinases.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIGURE 3. Specific interaction between active site residues
and HBPS. A, stereo view of HBPS bound to the active site. HBPS
binds the active site mainly by hydrophobic interactions.
Hydrogen bonds are indicated by the dashed lines. HBPS and
residues in hydrophobic contacts with HBPS are labeled. Color
scheme of the ribbon model is as in Fig. 2B. B, stereo view of
the hydrogen bond network at the sulfinate group of HBPS.
Hydrogen bonds are depicted with the dashed lines.
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIGURE 4. Proposed reaction mechanism of DszB. The
phenyl-hydroxy moieties of substrates are omitted for clarity.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
32534-32539)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Calzada,
M.T.Zamarro,
A.Alcón,
V.E.Santos,
E.Díaz,
J.L.García,
and
F.Garcia-Ochoa
(2009).
Analysis of dibenzothiophene desulfurization in a recombinant Pseudomonas putida strain.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
75,
875-877.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ohshiro,
S.Nakura,
Y.Ishii,
K.Kino,
K.Kirimura,
and
Y.Izumi
(2009).
Novel reactivity of dibenzothiophene monooxygenase from Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
73,
2128-2130.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Kilbane,
and
J.Robbins
(2007).
Characterization of the dszABC genes of Gordonia amicalis F.5.25.8 and identification of conserved protein and DNA sequences.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
75,
843-851.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ohshiro,
R.Ohkita,
T.Takikawa,
M.Manabe,
W.C.Lee,
M.Tanokura,
and
Y.Izumi
(2007).
Improvement of 2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate desulfinase, an enzyme involved in the dibenzothiophene desulfurization pathway, from Rhodococcus erythropolis KA2-5-1 by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
71,
2815-2821.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

