 |
PDBsum entry 2cin

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.36
- L-lysine 6-transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Lysine catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-lysine + 2-oxoglutarate = (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
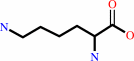 L-lysine
L-lysine
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
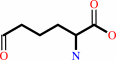 (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
|
+
|
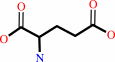 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
362:877-886
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Direct evidence for a glutamate switch necessary for substrate recognition: crystal structures of lysine epsilon-aminotransferase (Rv3290c) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv.
|
|
S.Mani Tripathi,
R.Ramachandran.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Lysine epsilon-aminotransferase (LAT) is a PLP-dependent enzyme that is highly
up-regulated in nutrient-starved tuberculosis models. It catalyzes an overall
reaction involving the transfer of the epsilon-amino group of L-lysine to
alpha-ketoglutarate to yield L-glutamate and
alpha-aminoadipate-delta-semialdehyde. We have cloned and characterized the
enzyme from Mycobacterium tuberculosisH37Rv. We report here the crystal
structures of the enzyme, the first from any source, in the unliganded form,
external aldimine with L-lysine, with bound PMP and with its C5 substrate
alpha-ketoglutarate. In addition to interaction details in the active site, the
structures reveal a Glu243 "switch" through which the enzyme changes
substrate specificities. The unique substrate L-lysine is recognized
specifically when Glu243 maintains a salt-bridge with Arg422. On the other hand,
the binding of the common C5 substrates L-glutamate and alpha-ketoglutarate is
enabled when Glu243 switches away and unshields Arg422. The structures reported
here, sequence conservation and earlier mutational studies suggest that the
"glutamate switch" is an elegant solution devised by a subgroup of
fold type I aminotransferases for recognition of structurally diverse substrates
in the same binding site and provides for reaction specificity.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. (a) The active site interactions shown in
split-stereo. An external aldimine with l-lysine and (b)
α-ketoglutarate-bound crystals. Oxygen and nitrogen atoms are
depicted in red and blue, respectively, for the protein and
ligands/cofactor. Carbon atoms from the same subunit are colored
yellow while those of the dimeric counterpart are colored green.
Carbon atoms of the co-factor/ligand are in pink, while water
oxygen atoms are shown as cyan balls. Polar interactions are
depicted by dotted lines. The movement of E243 on binding
α-ketoglutarate is indicated by a curved arrow (c)
Superposition of the active sites in PMP bound, l-lysine bound,
α-ketoglutarate bound and internal aldimine forms. The protein
chains in the respective structures are colored green, blue,
yellow and pink, while the modeled glutamate is indicated in
red. The Glu243 switch is indicated by a bold arrow. The
movement of the PLP moiety between the unliganded and liganded
forms is shown by a dotted arrow. A dotted circle indicates that
the O-5 of α-ketoglutarate and N of the modeled glutamate have
the correct spatial disposition to form an external aldimine
with PLP. Crosses represent water molecules in the different
crystal forms.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2006,
362,
877-886)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Taneja,
J.Yadav,
T.K.Chakraborty,
and
S.K.Brahmachari
(2009).
An Indian effort towards affordable drugs: "generic to designer drugs".
|
| |
Biotechnol J,
4,
348-360.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Murphy,
and
J.R.Brown
(2007).
Identification of gene targets against dormant phase Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.
|
| |
BMC Infect Dis,
7,
84.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Shrivastava,
and
R.Ramachandran
(2007).
Mechanistic insights from the crystal structures of a feast/famine regulatory protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
35,
7324-7335.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

