 |
PDBsum entry 2a0f

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase regulator
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2a0f
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
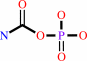 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
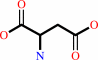 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
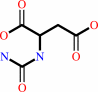 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 44.44% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
352:478-486
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of the E.coli aspartate transcarbamoylase trapped in the middle of the catalytic cycle.
|
|
K.A.Stieglitz,
K.J.Dusinberre,
J.P.Cardia,
H.Tsuruta,
E.R.Kantrowitz.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Snapshots of the catalytic cycle of the allosteric enzyme aspartate
transcarbamoylase have been obtained via X-ray crystallography. The enzyme in
the high-activity high-affinity R state contains two catalytic chains in the
asymmetric unit that are different. The active site in one chain is empty, while
the active site in the other chain contains an analog of the first substrate to
bind in the ordered mechanism of the reaction. Small angle X-ray scattering
shows that once the enzyme is converted to the R state, by substrate binding,
the enzyme remains in the R state until substrates are exhausted. Thus, this
structure represents the active form of the enzyme trapped at two different
stages in the catalytic cycle, before the substrates bind (or after the products
are released), and after the first substrate binds. Opening and closing of the
catalytic chain domains explains how the catalytic cycle occurs while the enzyme
remains globally in the R-quaternary structure.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Stereoviews of the active site of the R236_PAM
structure. (a) A simulated annealing 2F[o]−F[c] electron
density map, contoured at 1.8σ, with PAM (magenta) omitted from
the map calculation. Overlaid onto the electron density map are
the refined positions of the residues. (b) Overlay of the
active sites of the C1 (carbon atoms in light gray) and C6
(carbon atoms in dark gray) chains of the R[236_PAM] structure.
The interactions between the enzyme and PAM in the C1 chain are
shown as dotted lines. An asterisk after the residue number
indicates that the residue is donated from the adjacent C2
chain. Figure 3. Stereoviews of the active site of the
R236_PAM structure. (a) A simulated annealing 2F[o]−F[c]
electron density map, contoured at 1.8σ, with PAM (magenta)
omitted from the map calculation. Overlaid onto the electron
density map are the refined positions of the residues. (b)
Overlay of the active sites of the C1 (carbon atoms in light
gray) and C6 (carbon atoms in dark gray) chains of the
R[236_PAM] structure. The interactions between the enzyme and
PAM in the C1 chain are shown as dotted lines. An asterisk after
the residue number indicates that the residue is donated from
the adjacent C2 chain.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Complete active site of the C1 chain of the
R[236_PAM] structure with PAM bound. The Asp shown is based on
the position obtained using AUTODOCK.^14 The red arrow indicates
the attack of the α-amino group of Asp onto the carbonyl
carbon of PAM (distance 3.5 Å). Interactions to PAM and
Asp are shown by black and red dotted lines respectively.
Figure 4. Complete active site of the C1 chain of the R[236_PAM]
structure with PAM bound. The Asp shown is based on the position
obtained using AUTODOCK.[3]^14 The red arrow indicates the
attack of the α-amino group of Asp onto the carbonyl carbon of
PAM (distance 3.5 Å). Interactions to PAM and Asp are
shown by black and red dotted lines respectively. This Figure
was produced using POVScript+.[4]^33
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2005,
352,
478-486)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Stieglitz,
J.Xia,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2009).
The first high pH structure of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
74,
318-327.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wang,
J.Eldo,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Structural model of the R state of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase with substrates bound.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
371,
1261-1273.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Fetler,
E.R.Kantrowitz,
and
P.Vachette
(2007).
Direct observation in solution of a preexisting structural equilibrium for a mutant of the allosteric aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
495-500.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Eldo,
J.P.Cardia,
E.M.O'Day,
J.Xia,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2006).
N-phosphonacetyl-L-isoasparagine a potent and specific inhibitor of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
49,
5932-5938.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

