 |
PDBsum entry 1y2m

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from yeast rhododporidium toruloides
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Rhodosporidium toruloides. Organism_taxid: 5286. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.159
|
R-free:
|
0.187
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.Wang,A.Gamez,C.N.Sarkissian,M.Straub,M.G.Patch,G.W.Han,C.R.Scriver, R.C.Stevens
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
L.Wang
et al.
(2005).
Structure-based chemical modification strategy for enzyme replacement treatment of phenylketonuria.
Mol Genet Metab,
86,
134-140.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Nov-04
|
Release date:
|
01-Nov-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P11544
(PALY_RHOTO) -
Phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase from Rhodotorula toruloides
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
716 a.a.
665 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.25
- phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-phenylalanine = (E)-cinnamate + NH4+
|
|
2.
|
L-tyrosine = (E)-4-coumarate + NH4+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
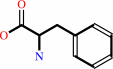 L-phenylalanine
L-phenylalanine
|
=
|
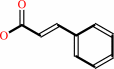 (E)-cinnamate
(E)-cinnamate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
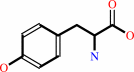 L-tyrosine
L-tyrosine
|
=
|
(E)-4-coumarate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
MIO
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Mol Genet Metab
86:134-140
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure-based chemical modification strategy for enzyme replacement treatment of phenylketonuria.
|
|
L.Wang,
A.Gamez,
C.N.Sarkissian,
M.Straub,
M.G.Patch,
G.W.Han,
S.Striepeke,
P.Fitzpatrick,
C.R.Scriver,
R.C.Stevens.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Structure-based protein engineering coupled with chemical modifications (e.g.,
pegylation) is a powerful combination to significantly improve the development
of proteins as therapeutic agents. As a test case, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
(PAL, EC 4.3.1.5) was selected for enzyme replacement therapy in phenylketonuria
[C.R. Scriver, S. Kaufman, Hyperphenylalaninemia:phenylalanine Hydroxylase
Deficiency. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, McGraw-Hill,
New York, 2001, Chapter 77], an inherited metabolic disorder (OMIM 261600)
causing mental retardation due to deficiency of the enzyme l-phenylalanine
hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.1). Previous in vivo studies of recombinant PAL
demonstrated a lowering of blood l-phenylalanine levels; yet, the metabolic
effect was not sustained due to protein degradation and immunogenicity [C.N.
Sarkissian, Z. Shao, F. Blain, R. Peevers, H. Su, R. Heft, T.M. Chang, C.R.
Scriver, A different approach to treatment of phenylketonuria:phenylalanine
degradation with recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA 96 (1999) 2339; J.A. Hoskins, G. Jack, H.E. Wade, R.J. Peiris, E.C. Wright,
D.J. Starr, J. Stern, Enzymatic control of phenylalanine intake in
phenylketonuria, Lancet 1 (1980) 392; C.M. Ambrus, S. Anthone, C. Horvath, K.
Kalghatgi, A.S. Lele, G. Eapen, J.L. Ambrus, A.J. Ryan, P. Li, Extracorporeal
enzyme reactors for depletion of phenylalanine in phenylketonuria, Ann. Intern.
Med. 106 (1987) 531]. Here, we report the 1.6A three-dimensional structure of
Rhodosporidium toruloides PAL, structure-based molecular engineering, pegylation
of PAL, as well as in vitro and in vivo PKU mouse model studies on pegylated PAL
formulations. Our results show that pegylation of R. toruloides PAL leads to
promising therapeutic efficacy after subcutaneous injection by enhancing the in
vivo activity, lowering plasma phenylalanine, and leading to reduced
immunogenicity. The three-dimensional structure of PAL provides a basis for
understanding the properties of pegylated forms of PAL and strategies for
structure-based re-engineering of PAL for PKU treatment.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Zano,
R.Malik,
S.Szucs,
R.Matalon,
and
R.E.Viola
(2011).
Modification of aspartoacylase for potential use in enzyme replacement therapy for the treatment of Canavan disease.
|
| |
Mol Genet Metab,
102,
176-180.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Kang,
and
R.C.Stevens
(2009).
Structural aspects of therapeutic enzymes to treat metabolic disorders.
|
| |
Hum Mutat,
30,
1591-1610.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.N.Sarkissian,
A.Gámez,
L.Wang,
M.Charbonneau,
P.Fitzpatrick,
J.F.Lemontt,
B.Zhao,
M.Vellard,
S.M.Bell,
C.Henschell,
A.Lambert,
L.Tsuruda,
R.C.Stevens,
and
C.R.Scriver
(2008).
Preclinical evaluation of multiple species of PEGylated recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase for the treatment of phenylketonuria.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
20894-20899.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Wang,
A.Gamez,
H.Archer,
E.E.Abola,
C.N.Sarkissian,
P.Fitzpatrick,
D.Wendt,
Y.Zhang,
M.Vellard,
J.Bliesath,
S.M.Bell,
J.F.Lemontt,
C.R.Scriver,
and
R.C.Stevens
(2008).
Structural and biochemical characterization of the therapeutic Anabaena variabilis phenylalanine ammonia lyase.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
380,
623-635.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Doggrell
(2008).
Is sapropterin treatment suitable for all subjects with phenylketonuria?
|
| |
Expert Opin Pharmacother,
9,
145-147.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Wang,
S.Surendran,
K.Michals-Matalon,
G.Bhatia,
S.Tanskley,
R.Koch,
J.Grady,
S.K.Tyring,
R.C.Stevens,
F.Guttler,
and
R.Matalon
(2007).
Mutations in the regulatory domain of phenylalanine hydroxylase and response to tetrahydrobiopterin.
|
| |
Genet Test,
11,
174-178.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Moffitt,
G.V.Louie,
M.E.Bowman,
J.Pence,
J.P.Noel,
and
B.S.Moore
(2007).
Discovery of two cyanobacterial phenylalanine ammonia lyases: kinetic and structural characterization.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
1004-1012.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Eavri,
and
H.Lorberboum-Galski
(2007).
A novel approach for enzyme replacement therapy. The use of phenylalanine hydroxylase-based fusion proteins for the treatment of phenylketonuria.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
23402-23409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Xue,
M.McCluskey,
K.Cantera,
F.S.Sariaslani,
and
L.Huang
(2007).
Identification, characterization and functional expression of a tyrosine ammonia-lyase and its mutants from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides.
|
| |
J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol,
34,
599-604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.V.Louie,
M.E.Bowman,
M.C.Moffitt,
T.J.Baiga,
B.S.Moore,
and
J.P.Noel
(2006).
Structural determinants and modulation of substrate specificity in phenylalanine-tyrosine ammonia-lyases.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
13,
1327-1338.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Pilbák,
A.Tomin,
J.Rétey,
and
L.Poppe
(2006).
The essential tyrosine-containing loop conformation and the role of the C-terminal multi-helix region in eukaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyases.
|
| |
FEBS J,
273,
1004-1019.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

