 |
PDBsum entry 1w2x

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.4.14
- biotin carboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-biotinyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + hydrogencarbonate + ATP = N6- carboxybiotinyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-biotinyl-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
N(6)- carboxybiotinyl-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.6.4.1.2
- acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + acetyl-CoA + ATP = malonyl-CoA + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
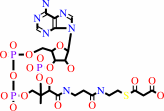 malonyl-CoA
malonyl-CoA
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Biotin
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
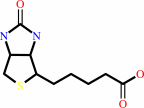 Biotin
Biotin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
12:1683-1691
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in complex with CP-640186.
|
|
H.Zhang,
B.Tweel,
J.Li,
L.Tong.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylases (ACCs) are important targets for the development
of therapeutic agents against obesity, diabetes, and other diseases. CP-640186
is a potent inhibitor of mammalian ACCs and can reduce body weight and improve
insulin sensitivity in test animals. It is believed to target the
carboxyltransferase (CT) domain of these enzymes. Here we report the crystal
structure of the yeast CT domain in complex with CP-640186. The inhibitor is
bound in the active site at the interface of a dimer of the CT domain. CP-640186
has tight interactions with the putative biotin binding site in the CT domain
and demonstrates a distinct mode of inhibiting the CT activity as compared to
the herbicides that inhibit plant ACCs. The affinity of inhibitors for the CT
domain has been assessed using kinetic and fluorescence anisotropy binding
studies. The structural information identifies three regions for drug binding in
the active site of CT.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Three Distinct Binding Regions in the Active Site
of CT(A) Molecular surface of the active site region of yeast
CT. The CoA and CP-640186 molecules are shown in gray and gold,
respectively. This panel was produced with Grasp (Nicholls et
al., 1991).(B) Comparison of the binding modes of CP-640186 (in
gold), haloxyfop (black), and CoA (gray). This panel was
produced with Ribbons (Carson, 1987).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2004,
12,
1683-1691)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Bengtsson,
S.Blaho,
D.B.Saitton,
K.Brickmann,
J.Broddefalk,
O.Davidsson,
T.Drmota,
R.Folmer,
K.Hallberg,
S.Hallén,
R.Hovland,
E.Isin,
P.Johannesson,
B.Kull,
L.O.Larsson,
L.Löfgren,
K.E.Nilsson,
T.Noeske,
N.Oakes,
A.T.Plowright,
V.Schnecke,
P.Ståhlberg,
P.Sörme,
H.Wan,
E.Wellner,
and
L.Oster
(2011).
Design of small molecule inhibitors of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 and 2 showing reduction of hepatic malonyl-CoA levels in vivo in obese Zucker rats.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
19,
3039-3053.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Marjanovic,
D.Chalupska,
C.Patenode,
A.Coster,
E.Arnold,
A.Ye,
G.Anesi,
Y.Lu,
I.Okun,
S.Tkachenko,
R.Haselkorn,
and
P.Gornicki
(2010).
Recombinant yeast screen for new inhibitors of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 identifies potential drugs to treat obesity.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
9093-9098.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.P.Madauss,
W.A.Burkhart,
T.G.Consler,
D.J.Cowan,
W.K.Gottschalk,
A.B.Miller,
S.A.Short,
T.B.Tran,
and
S.P.Williams
(2009).
The human ACC2 CT-domain C-terminus is required for full functionality and has a novel twist.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
449-461.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Xiang,
M.M.Callaghan,
K.G.Watson,
and
L.Tong
(2009).
A different mechanism for the inhibition of the carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase by tepraloxydim.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
20723-20727.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Y.Hu,
Y.C.Huang,
H.T.Yu,
and
Y.Zhang
(2008).
(Anthracen-9-yl)(piperidin-1-yl)-methanone.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online,
64,
o2120.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.B.Patil,
S.D.Minteer,
A.A.Mielke,
L.R.Lewis,
C.A.Casmaer,
E.J.Barrientos,
J.S.Ju,
J.L.Smith,
and
J.S.Fisher
(2007).
Malonyl coenzyme A affects insulin-stimulated glucose transport in myotubes.
|
| |
Arch Physiol Biochem,
113,
13-24.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Tong,
and
H.J.Harwood
(2006).
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylases: versatile targets for drug discovery.
|
| |
J Cell Biochem,
99,
1476-1488.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Shen,
C.Y.Chou,
G.G.Chang,
and
L.Tong
(2006).
Is dimerization required for the catalytic activity of bacterial biotin carboxylase?
|
| |
Mol Cell,
22,
807-818.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Shen,
S.L.Volrath,
S.C.Weatherly,
T.D.Elich,
and
L.Tong
(2004).
A mechanism for the potent inhibition of eukaryotic acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase by soraphen A, a macrocyclic polyketide natural product.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
16,
881-891.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

