 |
PDBsum entry 1sci

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.2.47
- (S)-hydroxynitrile lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a monosubstituted aliphatic (S)-hydroxynitrile = an aldehyde + hydrogen cyanide
|
|
2.
|
a disubstituted aliphatic (S)-hydroxynitrile = a ketone + hydrogen cyanide
|
|
3.
|
an aromatic (S)-hydroxynitrile = an aromatic aldehyde + hydrogen cyanide
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
monosubstituted aliphatic (S)-hydroxynitrile
|
=
|
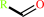 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 hydrogen cyanide
hydrogen cyanide
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
disubstituted aliphatic (S)-hydroxynitrile
|
=
|
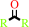 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 hydrogen cyanide
hydrogen cyanide
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
aromatic (S)-hydroxynitrile
|
=
|
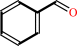 aromatic aldehyde
aromatic aldehyde
|
+
|
 hydrogen cyanide
hydrogen cyanide
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:20501-20510
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Reaction mechanism of hydroxynitrile lyases of the alpha/beta-hydrolase superfamily: the three-dimensional structure of the transient enzyme-substrate complex certifies the crucial role of LYS236.
|
|
K.Gruber,
G.Gartler,
B.Krammer,
H.Schwab,
C.Kratky.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The hydroxynitrile lyases (HNLs) from Hevea brasiliensis (HbHNL) and from
Manihot esculenta (MeHNL) are both members of the alpha/beta-hydrolase
superfamily. Mechanistic proposals have been put forward in the past for both
enzymes; they differed with respect to the role of the active-site lysine
residue for which a catalytic function was claimed for the Hevea enzyme but
denied for the Manihot enzyme. We applied a freeze-quench method to prepare
crystals of the complex of HbHNL with the biological substrate acetone
cyanohydrin and determined its three-dimensional structure. Site-directed
mutagenesis was used to prepare the mutant K236L, which is inactive although its
three-dimensional structure is similar to the wild-type enzyme. However, the
structure of the K236L-acetone cyanohydrin complex shows the substrate in a
different orientation from the wild-type complex. Finite difference
Poisson-Boltzmann calculations show that in the absence of Lys(236) the
catalytic base His(235) would be protonated at neutral pH. All of this suggests
that Lys(236) is instrumental for catalysis in several ways, i.e. by correctly
positioning the substrate, by stabilizing the negatively charged reaction
product CN(-), and by modulating the basicity of the catalytic base. These data
complete the elucidation of the reaction mechanism of alpha/beta-hydrolase HNLs,
in which the catalytic triad acts as a general base rather than as a
nucleophile; proton abstraction from the substrate is performed by the serine,
and reprotonation of the product cyanide is performed by the histidine residues.
Together with a threonine side chain, the active-site serine and lysine are also
involved in substrate binding.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIG. 2. The proposed mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by
HbHNL formulated for the cyanohydrin cleavage direction (21).
|
 |
Figure 3.
FIG. 3. The mechanism proposed for the reaction catalyzed
by MeHNL (24).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
20501-20510)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Paravidino,
M.J.Sorgedrager,
R.V.Orru,
and
U.Hanefeld
(2010).
Activity and enantioselectivity of the hydroxynitrile lyase MeHNL in dry organic solvents.
|
| |
Chemistry,
16,
7596-7604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Steiner,
H.J.Janssen,
P.Roversi,
A.J.Oakley,
and
S.Fetzner
(2010).
Structural basis for cofactor-independent dioxygenation of N-heteroaromatic compounds at the alpha/beta-hydrolase fold.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
657-662.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Kourist,
H.Jochens,
S.Bartsch,
R.Kuipers,
S.K.Padhi,
M.Gall,
D.Böttcher,
H.J.Joosten,
and
U.T.Bornscheuer
(2010).
The alpha/beta-hydrolase fold 3DM database (ABHDB) as a tool for protein engineering.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
1635-1643.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Padhi,
R.Fujii,
G.A.Legatt,
S.L.Fossum,
R.Berchtold,
and
R.J.Kazlauskas
(2010).
Switching from an esterase to a hydroxynitrile lyase mechanism requires only two amino acid substitutions.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
17,
863-871.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
d.e. .L.T.Yin,
P.Bernhardt,
K.L.Morley,
Y.Jiang,
J.D.Cheeseman,
V.Purpero,
J.D.Schrag,
and
R.J.Kazlauskas
(2010).
Switching catalysis from hydrolysis to perhydrolysis in Pseudomonas fluorescens esterase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
1931-1942.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Dreveny,
A.S.Andryushkova,
A.Glieder,
K.Gruber,
and
C.Kratky
(2009).
Substrate binding in the FAD-dependent hydroxynitrile lyase from almond provides insight into the mechanism of cyanohydrin formation and explains the absence of dehydrogenation activity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
3370-3377.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.von Langermann,
J.K.Guterl,
M.Pohl,
H.Wajant,
and
U.Kragl
(2008).
Hydroxynitrile lyase catalyzed cyanohydrin synthesis at high pH-values.
|
| |
Bioprocess Biosyst Eng,
31,
155-161.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Luo,
W.W.Han,
Y.H.Zhou,
Y.Yao,
and
Z.S.Li
(2008).
The 3D structure of the defense-related rice protein Pir7b predicted by homology modeling and ligand binding studies.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
14,
559-569.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.P.Hausinger
(2007).
New insights into acetone metabolism.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
671-673.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Purkarthofer,
W.Skranc,
C.Schuster,
and
H.Griengl
(2007).
Potential and capabilities of hydroxynitrile lyases as biocatalysts in the chemical industry.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
76,
309-320.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Purkarthofer,
K.Gruber,
M.Gruber-Khadjawi,
K.Waich,
W.Skranc,
D.Mink,
and
H.Griengl
(2006).
A biocatalytic Henry reaction--the hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis also catalyzes nitroaldol reactions.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
45,
3454-3456.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Forouhar,
Y.Yang,
D.Kumar,
Y.Chen,
E.Fridman,
S.W.Park,
Y.Chiang,
T.B.Acton,
G.T.Montelione,
E.Pichersky,
D.F.Klessig,
and
L.Tong
(2005).
Structural and biochemical studies identify tobacco SABP2 as a methyl salicylate esterase and implicate it in plant innate immunity.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
1773-1778.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Xu,
M.H.Zong,
Y.Y.Liu,
J.He,
Y.Y.Zhang,
and
W.Y.Lou
(2004).
Enzymatic enantioselective transcyanation of silicon-containing aliphatic ketone with (S)-hydroxynitrile lyase from Manihot esculenta.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
66,
27-33.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

