 |
PDBsum entry 1n8p

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of cystathionine gamma-lyase from yeast
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cystathionine gamma-lyase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: gamma-cystathionase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Baker's yeast. Organism_taxid: 4932. Gene: cys3. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.253
|
R-free:
|
0.346
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Messerschmidt,M.Worbs,C.Steegborn,M.C.Wahl,R.Huber,T.Clausen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Messerschmidt
et al.
(2003).
Determinants of enzymatic specificity in the Cys-Met-metabolism PLP-dependent enzymes family: crystal structure of cystathionine gamma-lyase from yeast and intrafamiliar structure comparison.
Biol Chem,
384,
373-386.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Nov-02
|
Release date:
|
04-Dec-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P31373
(CYS3_YEAST) -
Cystathionine gamma-lyase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
394 a.a.
393 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.4.1.1
- cystathionine gamma-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L,L-cystathionine + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + L-cysteine + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L,L-cystathionine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
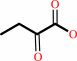 2-oxobutanoate
2-oxobutanoate
|
+
|
 L-cysteine
L-cysteine
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biol Chem
384:373-386
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Determinants of enzymatic specificity in the Cys-Met-metabolism PLP-dependent enzymes family: crystal structure of cystathionine gamma-lyase from yeast and intrafamiliar structure comparison.
|
|
A.Messerschmidt,
M.Worbs,
C.Steegborn,
M.C.Wahl,
R.Huber,
B.Laber,
T.Clausen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of cystathionine gamma-lyase (CGL) from yeast has been
solved by molecular replacement at a resolution of 2.6 A. The molecule consists
of 393 amino acid residues and one PLP moiety and is arranged in the crystal as
a tetramer with D2 symmetry as in other related enzymes of the
Cys-Met-metabolism PLP-dependent family like cystathionine beta-lyase (CBL). A
structure comparison with other family members revealed surprising insights into
the tuning of enzymatic specificity between the different family members. CGLs
from yeast or human are virtually identical at their active sites to
cystathionine gamma-synthase (CGS) from E. coli. Both CGLs and bacterial CGSs
exhibit gamma-synthase and gamma-lyase activities depending on their position in
the metabolic pathway and the available substrates. This group of enzymes has a
glutamate (E333 in yeast CGL) which binds to the distal group of cystathionine
(CTT) or the amino group of cysteine. Plant CGSs use homoserine phosphate
instead of O-succinyl-homoserine as one substrate. This is reflected by a
partially different active site structure in plant CGSs. In CGL and CBL the
pseudosymmetric substrate must dock at the active site in different
orientations, with S in gamma-position (CBL) or in delta-position (CGL). The
conserved glutamate steers the substrate as seen in other CGLs. In CBLs this
position is occupied by either tyrosine or hydrophobic residues directing
binding of CTT such that S is in the in gamma-position. In methionine
gamma-lyase a hydrophic patch operates as recognition site for the methyl group
of the methionine substrate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.S.El-Sayed
(2010).
Microbial L-methioninase: production, molecular characterization, and therapeutic applications.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
86,
445-467.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.H.Lodha,
A.F.Jaworski,
and
S.M.Aitken
(2010).
Characterization of site-directed mutants of residues R58, R59, D116, W340 and R372 in the active site of E. coli cystathionine beta-lyase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
19,
383-391.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Farsi,
P.H.Lodha,
J.E.Skanes,
H.Los,
N.Kalidindi,
and
S.M.Aitken
(2009).
Interconversion of a pair of active-site residues in Escherichia coli cystathionine gamma-synthase, E. coli cystathionine beta-lyase, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae cystathionine gamma-lyase and development of tools for the investigation of their mechanisms and reaction specificity.
|
| |
Biochem Cell Biol,
87,
445-457.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Sun,
R.Collins,
S.Huang,
L.Holmberg-Schiavone,
G.S.Anand,
C.H.Tan,
S.van-den-Berg,
L.W.Deng,
P.K.Moore,
T.Karlberg,
and
J.Sivaraman
(2009).
Structural Basis for the Inhibition Mechanism of Human Cystathionine {gamma}-Lyase, an Enzyme Responsible for the Production of H2S.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
3076-3085.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Lo,
M.S.Turner,
D.G.Barry,
R.Sreekumar,
T.P.Walsh,
and
P.M.Giffard
(2009).
Cystathionine gamma-lyase is a component of cystine-mediated oxidative defense in Lactobacillus reuteri BR11.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
1827-1837.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Nikulin,
S.Revtovich,
E.Morozova,
N.Nevskaya,
S.Nikonov,
M.Garber,
and
T.Demidkina
(2008).
High-resolution structure of methionine gamma-lyase from Citrobacter freundii.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
211-218.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Kudou,
S.Misaki,
M.Yamashita,
T.Tamura,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Inagaki
(2008).
The role of cysteine 116 in the active site of the antitumor enzyme L-methionine gamma-lyase from Pseudomonas putida.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
72,
1722-1730.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Zhu,
A.Lin,
and
R.Banerjee
(2008).
Kinetic properties of polymorphic variants and pathogenic mutants in human cystathionine gamma-lyase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
6226-6232.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.O.Rosado,
M.Salvador,
and
D.Bonatto
(2007).
Importance of the trans-sulfuration pathway in cancer prevention and promotion.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biochem,
301,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Ali,
and
T.Nozaki
(2007).
Current therapeutics, their problems, and sulfur-containing-amino-acid metabolism as a novel target against infections by "amitochondriate" protozoan parasites.
|
| |
Clin Microbiol Rev,
20,
164-187.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.R.Wheeler,
N.G.Coldham,
L.Keating,
S.V.Gordon,
E.E.Wooff,
T.Parish,
and
R.G.Hewinson
(2005).
Functional demonstration of reverse transsulfuration in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex reveals that methionine is the preferred sulfur source for pathogenic Mycobacteria.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
8069-8078.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Amarita,
M.Yvon,
M.Nardi,
E.Chambellon,
J.Delettre,
and
P.Bonnarme
(2004).
Identification and functional analysis of the gene encoding methionine-gamma-lyase in Brevibacterium linens.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
70,
7348-7354.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

