 |
PDBsum entry 1el5

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1el5
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.3.1
- sarcosine oxidasee (formaldehyde-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
sarcosine + O2 + H2O = formaldehyde + glycine + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
sarcosine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 85.71% similarity
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
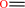 formaldehyde
formaldehyde
|
+
|
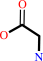 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
39:8813-8824
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Monomeric sarcosine oxidase: 1. Flavin reactivity and active site binding determinants.
|
|
M.A.Wagner,
P.Trickey,
Z.W.Chen,
F.S.Mathews,
M.S.Jorns.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Monomeric sarcosine oxidase (MSOX) is an inducible bacterial flavoenzyme that
catalyzes the oxidative demethylation of sarcosine (N-methylglycine) and
contains covalently bound FAD [8alpha-(S-cysteinyl)FAD]. This paper describes
the spectroscopic and thermodynamic properties of MSOX as well as the X-ray
crystallographic characterization of three new enzyme.inhibitor complexes. MSOX
stabilizes the anionic form of the oxidized flavin (pK(a) = 8.3 versus 10.4 with
free FAD), forms a thermodynamically stable flavin radical, and stabilizes the
anionic form of the radical (pK(a) < 6 versus pK(a) = 8.3 with free FAD).
MSOX forms a covalent flavin.sulfite complex, but there appears to be a
significant kinetic barrier against complex formation. Active site binding
determinants were probed in thermodynamic studies with various substrate
analogues whose binding was found to perturb the flavin absorption spectrum and
inhibit MSOX activity. The carboxyl group of sarcosine is essential for binding
since none is observed with simple amines. The amino group of sarcosine is not
essential, but binding affinity depends on the nature of the substitution
(CH(3)XCH(2)CO(2)(-), X = CH(2) < O < S < Se < Te), an effect which
has been attributed to differences in the strength of donor-pi interactions.
MSOX probably binds the zwitterionic form of sarcosine, as judged by the
spectrally similar complexes formed with dimethylthioacetate
[(CH(3))(2)S(+)CH(2)CO(2)(-)] and dimethylglycine (K(d) = 20.5 and 17.4 mM,
respectively) and by the crystal structure of the latter. The methyl group of
sarcosine is not essential but does contribute to binding affinity. The methyl
group contribution varied from -3.79 to -0.65 kcal/mol with CH(3)XCH(2)CO(2)(-)
depending on the nature of the heteroatom (NH(2)(+) > O > S) and appeared
to be inversely correlated with heteroatom electron density. Charge-transfer
complexes are formed with MSOX and CH(3)XCH(2)CO(2)(-) when X = S, Se, or Te. An
excellent linear correlation is observed between the energy of the charge
transfer bands and the one-electron reduction potentials of the ligands. The
presence of a sulfur, selenium, or telurium atom identically positioned with
respect to the flavin ring is confirmed by X-ray crystallography, although the
increased atomic radius of S < Se < Te appears to simultaneously favor an
alternate binding position for the heavier atoms. Although L-proline is a poor
substrate, aromatic heterocyclic carboxylates containing a five-membered ring
and various heteroatoms (X = NH, O, S) are good ligands (K(d, X=NH) = 1.37 mM)
and form charge-transfer complexes with MSOX. The energy of the charge-transfer
bands (S > O >> NH) is linearly correlated with the one-electron
ionization potentials of the corresponding heterocyclic rings.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Jorns,
Z.W.Chen,
and
F.S.Mathews
(2010).
Structural characterization of mutations at the oxygen activation site in monomeric sarcosine oxidase .
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
3631-3639.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Heinrich,
U.Diederichsen,
and
M.G.Rudolph
(2009).
Lys314 is a nucleophile in non-classical reactions of orotidine-5'-monophosphate decarboxylase.
|
| |
Chemistry,
15,
6619-6625.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Pedotti,
E.Rosini,
G.Molla,
T.Moschetti,
C.Savino,
B.Vallone,
and
L.Pollegioni
(2009).
Glyphosate resistance by engineering the flavoenzyme glycine oxidase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
36415-36423.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.R.Kommoju,
R.C.Bruckner,
P.Ferreira,
C.J.Carrell,
F.S.Mathews,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2009).
Factors that affect oxygen activation and coupling of the two redox cycles in the aromatization reaction catalyzed by NikD, an unusual amino acid oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
9542-9555.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ilari,
A.Bonamore,
S.Franceschini,
A.Fiorillo,
A.Boffi,
and
G.Colotti
(2008).
The X-ray structure of N-methyltryptophan oxidase reveals the structural determinants of substrate specificity.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
2065-2075.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Collard,
J.Zhang,
I.Nemet,
K.R.Qanungo,
V.M.Monnier,
and
V.C.Yee
(2008).
Crystal Structure of the Deglycating Enzyme Fructosamine Oxidase (Amadoriase II).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
27007-27016.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
R.C.Bruckner,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2008).
Identification of the oxygen activation site in monomeric sarcosine oxidase: role of Lys265 in catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
9124-9135.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Carrell,
R.C.Bruckner,
D.Venci,
G.Zhao,
M.S.Jorns,
and
F.S.Mathews
(2007).
NikD, an unusual amino acid oxidase essential for nikkomycin biosynthesis: structures of closed and open forms at 1.15 and 1.90 A resolution.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
928-941.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Ralph,
J.S.Hirschi,
M.A.Anderson,
W.W.Cleland,
D.A.Singleton,
and
P.F.Fitzpatrick
(2007).
Insights into the mechanism of flavoprotein-catalyzed amine oxidation from nitrogen isotope effects on the reaction of N-methyltryptophan oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
7655-7664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2006).
Spectral and kinetic characterization of the michaelis charge transfer complex in monomeric sarcosine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
5985-5992.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Hynson,
F.S.Mathews,
and
M.Schuman Jorns
(2006).
Identification of a stable flavin-thiolate adduct in heterotetrameric sarcosine oxidase.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
362,
656-663.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Hassan-Abdallah,
G.Zhao,
M.Eschenbrenner,
Z.W.Chen,
F.S.Mathews,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2005).
Cloning, expression and crystallization of heterotetrameric sarcosine oxidase from Pseudomonas maltophilia.
|
| |
Protein Expr Purif,
43,
33-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Hassan-Abdallah,
R.C.Bruckner,
G.Zhao,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2005).
Biosynthesis of covalently bound flavin: isolation and in vitro flavinylation of the monomeric sarcosine oxidase apoprotein.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
44,
6452-6462.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Ralph,
and
P.F.Fitzpatrick
(2005).
pH and kinetic isotope effects on sarcosine oxidation by N-methyltryptophan oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
44,
3074-3081.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2005).
Ionization of zwitterionic amine substrates bound to monomeric sarcosine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
44,
16866-16874.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Bottoms,
P.E.Smith,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2002).
A structurally conserved water molecule in Rossmann dinucleotide-binding domains.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
2125-2137.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
H.Song,
Z.W.Chen,
F.S.Mathews,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2002).
Monomeric sarcosine oxidase: role of histidine 269 in catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9751-9764.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2002).
Monomeric sarcosine oxidase: evidence for an ionizable group in the E.S complex.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9747-9750.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Job,
G.L.Marcone,
M.S.Pilone,
and
L.Pollegioni
(2002).
Glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis. Characterization of a new flavoprotein.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
6985-6993.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Binda,
R.Angelini,
R.Federico,
P.Ascenzi,
and
A.Mattevi
(2001).
Structural bases for inhibitor binding and catalysis in polyamine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
2766-2776.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Eschenbrenner,
L.J.Chlumsky,
P.Khanna,
F.Strasser,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2001).
Organization of the multiple coenzymes and subunits and role of the covalent flavin link in the complex heterotetrameric sarcosine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
5352-5367.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
J.Qu,
F.A.Davis,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2000).
Inactivation of monomeric sarcosine oxidase by reaction with N-(cyclopropyl)glycine.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
14341-14347.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

