 |
PDBsum entry 1bwp

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Probing the substrate specificity of the intracellular brain platelet- activating factor acetylhydrolase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Chain: a. Synonym: pafah. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Cattle. Organism_taxid: 9913. Organ: brain. Tissue: brain. Cellular_location: cytoplasm. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21. Expression_system_taxid: 511693.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Homo-Dimer (from PDB file)
Homo-Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.209
|
R-free:
|
0.252
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.S.Ho,P.J.Sheffield,J.Masuyama,H.Arai,J.Li,J.Aoki,K.Inoue, U.Derewenda,Z.Derewenda
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.S.Ho
et al.
(1999).
Probing the substrate specificity of the intracellular brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase.
Protein Eng,
12,
693-700.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Sep-98
|
Release date:
|
18-May-99
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q29460
(PA1B3_BOVIN) -
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit alpha1 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
232 a.a.
212 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.47
- 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-O-alkyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
1-O-alkyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
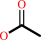 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Protein Eng
12:693-700
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Probing the substrate specificity of the intracellular brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase.
|
|
Y.S.Ho,
P.J.Sheffield,
J.Masuyama,
H.Arai,
J.Li,
J.Aoki,
K.Inoue,
U.Derewenda,
Z.S.Derewenda.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolases (PAF-AHs) are unique PLA2s which
hydrolyze the sn-2 ester linkage in PAF-like phospholipids with a marked
preference for very short acyl chains, typically acetyl. The recent solution of
the crystal structure of the alpha(1) catalytic subunit of isoform Ib of bovine
brain intracellular PAF-AH at 1.7 A resolution paved the way for a detailed
examination of the molecular basis of substrate specificity in this enzyme. The
crystal structure suggests that the side chains of Thr103, Leu48 and Leu194 are
involved in substrate recognition. Three single site mutants (L48A, T103S and
L194A) were overexpressed and their structures were solved to 2.3 A resolution
or better by X-ray diffraction methods. Enzyme kinetics showed that, compared
with wild-type protein, all three mutants have higher relative activity against
phospholipids with sn-2 acyl chains longer than an acetyl. However, for each of
the mutants we observed an unexpected and substantial reduction in the V(max) of
the reaction. These results are consistent with the model in which residues
Leu48, Thr103 and Leu194 indeed contribute to substrate specificity and in
addition suggest that the integrity of the specificity pocket is critical for
the expression of full catalytic function, thus conferring very high substrate
selectivity on the enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Almonacid,
E.R.Yera,
J.B.Mitchell,
and
P.C.Babbitt
(2010).
Quantitative comparison of catalytic mechanisms and overall reactions in convergently evolved enzymes: implications for classification of enzyme function.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
6,
e1000700.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.M.McIntyre,
S.M.Prescott,
and
D.M.Stafforini
(2009).
The emerging roles of PAF acetylhydrolase.
|
| |
J Lipid Res,
50,
S255-S259.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Martínez-Martínez,
J.Navarro-Fernández,
J.Daniel Lozada-Ramírez,
F.García-Carmona,
and
A.Sánchez-Ferrer
(2008).
YesT: a new rhamnogalacturonan acetyl esterase from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
379-388.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Quevillon-Cheruel,
N.Leulliot,
M.Graille,
N.Hervouet,
F.Coste,
H.Bénédetti,
C.Zelwer,
J.Janin,
and
H.Van Tilbeurgh
(2005).
Crystal structure of yeast YHR049W/FSH1, a member of the serine hydrolase family.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1350-1356.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Blouin,
D.Butt,
and
A.J.Roger
(2004).
Rapid evolution in conformational space: a study of loop regions in a ubiquitous GTP binding domain.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
608-616.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.C.Akoh,
G.C.Lee,
Y.C.Liaw,
T.H.Huang,
and
J.F.Shaw
(2004).
GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
43,
534-552.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Min,
C.Wilder,
J.Aoki,
H.Arai,
K.Inoue,
L.Paul,
and
M.H.Gelb
(2001).
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolases: broad substrate specificity and lipoprotein binding does not modulate the catalytic properties of the plasma enzyme.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
4539-4549.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Mølgaard,
S.Kauppinen,
and
S.Larsen
(2000).
Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
373-383.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

