 |
PDBsum entry 9atc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
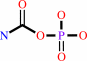 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
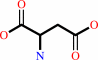 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
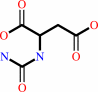 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Proteins
33:430-443
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Intersubunit hydrogen bond acts as a global molecular switch in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
|
Y.Ha,
N.M.Allewell.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Tyr 165 in the catalytic subunit of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase
(ATCase, EC 2.1.3.2) forms an intersubunit hydrogen bond in the T state with Glu
239 in the 240s loop of a second catalytic subunit, which is broken in the T to
R transition. Substitution of Tyr 165 by Phe lowers substrate affinity by
approximately an order of magnitude and alters the pH profile for enzyme
function. We have determined the crystal structure of Y165F at 2.4 A resolution
by molecular replacement, using a wild-type T state structure as the probe, and
refined it to an R value of 25.2%. The Y165F mutation induces a global
conformational change that is in the opposite direction to the T to R transition
and therefore results in an extreme T state. The two catalytic trimers move
closer by approximately 0.14 A and rotate by approximately 0.2 degrees , in the
opposite direction to the T-->R rotation; the two domains of each catalytic
chain rotate by approximately 2.1 degrees, also in the opposite direction to the
T-->R transition; and the 240s loop adopts a new conformation. Residues 229
to 236 shift by approximately 2.4 A so that the active site is more open.
Residues 237 to 244 rotate by approximately 24.1 degrees, altering interactions
within the 240s loop and at the C1-C4 and C1-R4 interfaces. Arg 167, a key
residue in domain closure and interactions with L-Asp, swings out from the
active site to interact with Tyr 197. This crystal structure is consistent with
the functional properties of Y165F, expands our knowledge of the conformational
repertoire of ATCase, and indicates that the canonical T state does not
represent an extreme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

