 |
PDBsum entry 8prv

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Cytosolic protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
8prv
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 1584 a.a.
1584 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 163 a.a.
163 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 2034 a.a.
2034 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Cytosolic protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Asymmetric unit of the yeast fatty acid synthase in the non-rotated state with acp at the ketosreductase domain (fasamn sample)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha. Chain: a, b. Fatty acid synthase subunit beta. Chain: g. Ec: 2.3.1.86,4.2.1.59,1.3.1.9,2.3.1.38,2.3.1.39,3.1.2.14
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Baker's yeast. Organism_taxid: 4932. Organism_taxid: 4932
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.Singh,G.Bunzel,B.Graf,K.M.Yip,H.Stark,A.Chari
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.Singh
et al.
(2023).
Reconstruction of a fatty acid synthesis cycle from a carrier protein and cofactor structural snapshots..
Cell,
186,
5054.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Jul-23
|
Release date:
|
22-Nov-23
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P19097
(FAS2_YEAST) -
Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1887 a.a.
1584 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.1.1.1.100
- 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] + NADP+ = a 3-oxoacyl-[ACP] + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
3-oxoacyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.3.1.41
- beta-ketoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase I.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a fatty acyl-[ACP] + malonyl-[ACP] + H+ = a 3-oxoacyl-[ACP] + holo- [ACP] + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
fatty acyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
malonyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
3-oxoacyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
holo- [ACP]
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains A, B, G:
E.C.2.3.1.86
- fatty-acyl-CoA synthase system.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetyl-CoA + n malonyl-CoA + 2n NADPH + 4n H+ = a long-chain-acyl-CoA + n CoA + n CO2 + 2n NADP+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
+
|
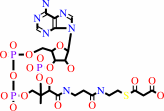 n
malonyl-CoA
n
malonyl-CoA
|
+
|
2n NADPH
|
+
|
4n H(+)
|
=
|
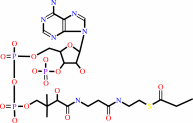 long-chain-acyl-CoA
long-chain-acyl-CoA
|
+
|
 n
CoA
n
CoA
|
+
|
 n
CO2
n
CO2
|
+
|
2n NADP(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
Chain G:
E.C.1.3.1.9
- enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2,3-saturated acyl-[ACP] + NAD+ = a (2E)-enoyl-[ACP] + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2,3-saturated acyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 n
NAD(+)
n
NAD(+)
|
=
|
(2E)-enoyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
Chain G:
E.C.2.3.1.38
- [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
holo-[ACP] + acetyl-CoA = acetyl-[ACP] + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
holo-[ACP]
|
+
|
 n
acetyl-CoA
n
acetyl-CoA
|
=
|
acetyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 7:
|
 |
Chain G:
E.C.2.3.1.39
- [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
holo-[ACP] + malonyl-CoA = malonyl-[ACP] + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
holo-[ACP]
|
+
|
 n
malonyl-CoA
n
malonyl-CoA
|
=
|
malonyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 8:
|
 |
Chain G:
E.C.3.1.2.14
- oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(9Z)-octadecenoyl-[ACP] + H2O = (9Z)-octadecenoate + holo-[ACP] + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
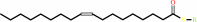 Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]
Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]
|
+
|
n
H(2)O
|
=
|
 [acyl-carrier-protein]
[acyl-carrier-protein]
|
+
|
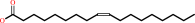 oleate
oleate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 9:
|
 |
Chain G:
E.C.4.2.1.59
- 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] = a (2E)-enoyl-[ACP] + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
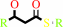 (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein]
(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein]
|
=
|
n
trans-2-enoyl-[acyl- carrier protein]
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
| |

