 |
PDBsum entry 7cuc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
7cuc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.7.3.3
- factor independent urate hydroxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
AMP Catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urate + O2 + H2O = 5-hydroxyisourate + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
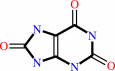 urate
urate
|
+
|
O2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 76.92% similarity
|
=
|
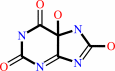 5-hydroxyisourate
5-hydroxyisourate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Copper
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.97
- 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
5-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-ureido-2,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylate + H+ = (S)-allantoin + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
5-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-ureido-2,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 66.67% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
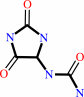 (S)-allantoin
(S)-allantoin
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biochem
169:15-23
(2021)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Identification of quasi-stable water molecules near the Thr73-Lys13 catalytic diad of Bacillus sp. TB-90 urate oxidase by X-ray crystallography with controlled humidity.
|
|
T.Hibi,
T.Itoh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Urate oxidases (UOs) catalyze the cofactor-independent oxidation of uric acid,
and an extensive water network in the active site has been suggested to play an
essential role in the catalysis. For our present analysis of the structure and
function of the water network, the crystal qualities of Bacillus sp. TB-90 urate
oxidase were improved by controlled dehydration using the humid air and
glue-coating method. After the dehydration, the P21212 crystals were transformed
into the I222 space group, leading to an extension of the maximum resolution to
1.42 Å. The dehydration of the crystals revealed a significant change in the
five-water-molecules' binding mode in the vicinity of the catalytic diad,
indicating that these molecules are quasi-stable. The pH profile analysis of
log(kcat) gave two pKa values: pKa1 at 6.07 ± 0.07 and pKa2 at
7.98 ± 0.13. The site-directed mutagenesis of K13, T73 and N276 involved in
the formation of the active-site water network revealed that the activities of
these mutant variants were significantly reduced. These structural and kinetic
data suggest that the five quasi-stable water molecules play an essential role
in the catalysis of the cofactor-independent urate oxidation by reducing the
energy penalty for the substrate-binding or an on-off switching for the
proton-relay rectification.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

