 |
PDBsum entry 7c7f

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
7c7f
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structures of akr1c3 binary complex with NADP+
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member c3. Chain: a, b. Synonym: trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: akr1c3, ddh1, hsd17b5, kiaa0119, pgfs. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.226
|
R-free:
|
0.268
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.Irie,N.Toyooka,S.Endo
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Endo
et al.
(2020).
Development of Novel AKR1C3 Inhibitors as New Potential Treatment for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.
J Med Chem,
63,
10396-10411.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-May-20
|
Release date:
|
23-Sep-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P42330
(AK1C3_HUMAN) -
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
323 a.a.
319 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.188
- prostaglandin-F synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
prostaglandin F2alpha + NADP+ = prostaglandin D2 + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
prostaglandin F2alpha
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
 prostaglandin D2
prostaglandin D2
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.210
- 3beta-(or 20alpha)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol + NADP+ = 17beta-hydroxy-5alpha- androstan-3-one + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
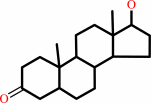 17beta-hydroxy-5alpha- androstan-3-one
17beta-hydroxy-5alpha- androstan-3-one
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.239
- 3alpha-(17beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
testosterone + NAD+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
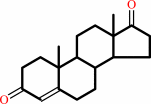 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.357
- 3alpha-hydroxysteroid 3-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a 3alpha-hydroxysteroid + NADP+ = a 3-oxosteroid + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a 3alpha-hydroxysteroid + NAD+ = a 3-oxosteroid + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
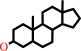 3alpha-hydroxysteroid
3alpha-hydroxysteroid
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 3-oxosteroid
3-oxosteroid
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 3alpha-hydroxysteroid
3alpha-hydroxysteroid
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
 3-oxosteroid
3-oxosteroid
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.53
- 3alpha(or 20beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol + NAD+ = 17beta-hydroxyandrostanone + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
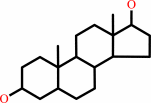 androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol
androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
17beta-hydroxyandrostanone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.62
- 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
17beta-estradiol + NAD+ = estrone + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
17beta-estradiol + NADP+ = estrone + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
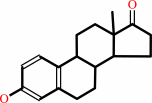 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 7:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.64
- testosterone 17beta-dehydrogenase (NADP(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
testosterone + NADP+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
63:10396-10411
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Development of Novel AKR1C3 Inhibitors as New Potential Treatment for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.
|
|
S.Endo,
H.Oguri,
J.Segawa,
M.Kawai,
D.Hu,
S.Xia,
T.Okada,
K.Irie,
S.Fujii,
H.Gouda,
K.Iguchi,
T.Matsukawa,
N.Fujimoto,
T.Nakayama,
N.Toyooka,
T.Matsunaga,
A.Ikari.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aldo-keto reductase (AKR) 1C3 catalyzes the synthesis of active androgens that
promote the progression of prostate cancer. AKR1C3 also contributes to
androgen-independent cell proliferation and survival through the metabolism of
prostaglandins and reactive aldehydes. Because of its elevation in
castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) tissues, AKR1C3 is a promising
therapeutic target for CRPC. In this study, we found a novel potent AKR1C3
inhibitor,
N-(4-fluorophenyl)-8-hydroxy-2-imino-2H-chromene-3-carboxamide
(2d), and synthesized its derivatives with IC50 values of
25-56 nM and >220-fold selectivity over other AKRs (1C1, 1C2, and 1C4). The
structural factors for the inhibitory potency were elucidated by
crystallographic study of AKR1C3 complexes with 2j and 2l. The
inhibitors suppressed proliferation of prostate cancer 22Rv1 and PC3 cells
through both androgen-dependent and androgen-independent mechanisms.
Additionally, 2j and 2l prevented prostate tumor growth in a
xenograft mouse model. Furthermore, the inhibitors significantly augmented
apoptotic cell death induced by anti-CRPC drugs (abiraterone or enzalutamide).

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

