 |
PDBsum entry 7c0c
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of azospirillum brasilense l-2-keto-3-deoxyarabonate dehydratase (apo form)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
L-2-keto-3-deoxyarabonate dehydratase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l. Synonym: l-kda dehydratase,2-dehydro-3-deoxy-l-arabinonate dehydratase,l-2-keto-3-deoxyarabinonate dehydratase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Azospirillum brasilense. Organism_taxid: 192. Gene: arad. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.255
|
R-free:
|
0.297
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Watanabe,R.Nobuchi,S.Watanabe
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Watanabe
et al.
(2020).
Biochemical and Structural Characterization of l-2-Keto-3-deoxyarabinonate Dehydratase: A Unique Catalytic Mechanism in the Class I Aldolase Protein Superfamily.
Biochemistry,
59,
2962-2973.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-May-20
|
Release date:
|
05-Aug-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q1JUQ0
(KDADA_AZOBR) -
L-2-keto-3-deoxyarabonate dehydratase from Azospirillum brasilense
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
309 a.a.
302 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.43
- 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-arabinonate dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-arabinonate = 2,5-dioxopentanoate + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
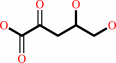 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-arabinonate
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-arabinonate
|
=
|
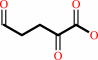 2,5-dioxopentanoate
2,5-dioxopentanoate
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
59:2962-2973
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Biochemical and Structural Characterization of l-2-Keto-3-deoxyarabinonate Dehydratase: A Unique Catalytic Mechanism in the Class I Aldolase Protein Superfamily.
|
|
S.Watanabe,
Y.Watanabe,
R.Nobuchi,
A.Ono.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
l-2-Keto-3-deoxyarabinonate (l-KDA) dehydratase (AraD) catalyzes the hydration
of l-KDA to α-ketoglutaric semialdehyde in the nonphosphorylative l-arabinose
pathway from bacteria and belongs to the dihydrodipicolinate synthase
(DHDPS)/N-acetylneuraminate lyase (NAL) protein superfamily. All members
of this superfamily, including several aldolases for l-KDA, share a common
catalytic mechanism of retro-aldol fission, in which a lysine residue forms a
Schiff base with the carbonyl C2 atom of the substrate, followed by proton
abstraction of the substrate by a tyrosine residue as the base catalyst. Only
AraD possesses a glutamine residue instead of this active site tyrosine,
suggesting its involvement in catalysis. We herein determined the crystal
structures of AraD from the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Azospirillum
brasilense and AraD in complex with β-hydroxypyruvate and 2-oxobutyrate,
two substrate analogues, at resolutions of 1.9, 1.6, and 2.2 Å, respectively.
In both of the complexed structures, the ε-nitrogen of the conserved Lys171 was
covalently linked to the carbonyl C2 atom of the ligand, which was consistent
with the Schiff base intermediate form, similar to other DHDPS/NAL members. A
site-directed mutagenic study revealed that Glu173 and Glu200 played important
roles as base catalysts, whereas Gln143 was not absolutely essential. The
abstraction of one of the C3 protons of the substrate (but not the O4 hydroxyl)
by Glu173 was similar to that by the (conserved) tyrosine residues in the two
DHDPS/NAL members that produce α-ketoglutaric semialdehyde
(d-5-keto-4-deoxygalactarate dehydratase and
Δ1-pyrroline-4-hydroxy-2-carboxylate deaminase), indicating that
these enzymes evolved convergently despite similarities in the overall reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

