 |
PDBsum entry 7bgc
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.8
- cholinesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acylcholine + H2O = a carboxylate + choline + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
acylcholine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 46.67% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
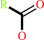 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
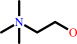 choline
choline
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
64:4972-4990
(2021)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Sustainable Drug Discovery of Multi-Target-Directed Ligands for Alzheimer's Disease.
|
|
M.Rossi,
M.Freschi,
L.de Camargo Nascente,
A.Salerno,
S.de Melo Viana Teixeira,
F.Nachon,
F.Chantegreil,
O.Soukup,
L.Prchal,
M.Malaguti,
C.Bergamini,
M.Bartolini,
C.Angeloni,
S.Hrelia,
L.A.Soares Romeiro,
M.L.Bolognesi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The multifactorial nature of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a reason for the lack
of effective drugs as well as a basis for the development of
"multi-target-directed ligands" (MTDLs). As cases increase in
developing countries, there is a need of new drugs that are not only effective
but also accessible. With this motivation, we report the first sustainable
MTDLs, derived from cashew nutshell liquid (CNSL), an inexpensive food waste
with anti-inflammatory properties. We applied a framework combination of
functionalized CNSL components and well-established acetylcholinesterase
(AChE)/butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) tacrine templates. MTDLs were selected based
on hepatic, neuronal, and microglial cell toxicity. Enzymatic studies disclosed
potent and selective AChE/BChE inhibitors (5, 6, and 12),
with subnanomolar activities. The X-ray crystal structure of 5 complexed
with BChE allowed rationalizing the observed activity (0.0352 nM). Investigation
in BV-2 microglial cells revealed antineuroinflammatory and neuroprotective
activities for 5 and 6 (already at 0.01 μM), confirming the
design rationale.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

