 |
PDBsum entry 6yok
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
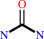 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Chemistry
26:16541-16553
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Direct Introduction of an Alkylsulfonamido Group on C-sites of Isomeric Dicarba-closo-dodecaboranes: The Influence of Stereochemistry on Inhibitory Activity against the Cancer-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase IX Isoenzyme.
|
|
J.Nekvinda,
M.Kugler,
J.Holub,
S.El Anwar,
J.Brynda,
K.Pospíšilová,
Z.Růžičková,
P.Řezáčová,
B.Grüner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX), a tumor-associated metalloenzyme, represents a
validated target for cancer therapy and diagnostics. Herein, we report the
inhibition properties of isomeric families of
sulfonamidopropyl-dicarba-closo-dodecaboranes group(s) prepared using a new
direct five-step synthesis from the corresponding parent cages. The protocol
offers a reliable solution for synthesis of singly and doubly substituted
dicarba-closo-dodecaboranes with a different geometric position of carbon atoms.
The closo-compounds from the ortho- and meta-series were then degraded to
corresponding 11-vertex dicarba-nido-undecaborate(1-) anions. All compounds show
in vitro enzymatic activity against CA IX in the low nanomolar or subnanomolar
range. This is accompanied by clear isomer dependence of the inhibition constant
(Ki ) and selectivity towards CA IX. Decreasing trends in
Ki and selectivity index (SI ) values are observed with
increasing separation of the cage carbon atoms. Interactions of compounds with
the active sites of CA IX were explored with X-ray crystallography, and eight
high-resolution crystal structures uncovered the structural basis of inhibition
potency and selectivity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

