 |
PDBsum entry 6yhc
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of chimeric carbonic anhydrase xii with 3- (benzylamino)-2,5,6-trifluoro-4-[(2-hydroxyethyl) sulfonyl]benzenesulfonamide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase 2. Chain: a. Synonym: carbonate dehydratase ii,carbonic anhydrasE C,cac,carbonic anhydrase ii,ca-ii. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ca2. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.28Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.135
|
R-free:
|
0.172
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Smirnov,E.Manakova,S.Grazulis
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Smirnovienė
et al.
(2021).
Switching the Inhibitor-Enzyme Recognition Profile via Chimeric Carbonic Anhydrase XII.
ChemistryOpen,
10,
567-580.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Mar-20
|
Release date:
|
07-Apr-21
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00918
(CAH2_HUMAN) -
Carbonic anhydrase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
260 a.a.
257 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 6 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
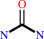 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
ChemistryOpen
10:567-580
(2021)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Switching the Inhibitor-Enzyme Recognition Profile via Chimeric Carbonic Anhydrase XII.
|
|
J.Smirnovienė,
A.Smirnov,
A.Zakšauskas,
A.Zubrienė,
V.Petrauskas,
A.Mickevičiūtė,
V.Michailovienė,
E.Čapkauskaitė,
E.Manakova,
S.Gražulis,
L.Baranauskienė,
W.Y.Chen,
J.E.Ladbury,
D.Matulis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A key part of the optimization of small molecules in pharmaceutical inhibitor
development is to vary the molecular design to enhance complementarity of
chemical features of the compound with the positioning of amino acids in the
active site of a target enzyme. Typically this involves iterations of synthesis,
to modify the compound, and biophysical assay, to assess the outcomes. Selective
targeting of the anti-cancer carbonic anhydrase isoform XII (CA XII), this
process is challenging because the overall fold is very similar across the
twelve CA isoforms. To enhance drug development for CA XII we used a reverse
engineering approach where mutation of the key six amino acids in the active
site of human CA XII into the CA II isoform was performed to provide a protein
chimera (chCA XII) which is amenable to structure-based compound optimization.
Through determination of structural detail and affinity measurement of the
interaction with over 60 compounds we observed that the compounds that bound CA
XII more strongly than CA II, switched their preference and bound more strongly
to the engineered chimera, chCA XII, based on CA II, but containing the 6 key
amino acids from CA XII, behaved as CA XII in its compound recognition profile.
The structures of the compounds in the chimeric active site also resembled those
determined for complexes with CA XII, hence validating this protein engineering
approach in the development of new inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

