
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 146 a.a.
146 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 2 more)
220 a.a.
(+ 2 more)
220 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 164 a.a.
164 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 74 a.a.
74 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Viral protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of the native full-length HIV-1 capsid protein in complex with cyclophilin a from helical assembly (-8,13)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Gag-pol polyprotein. Chain: a, b, c, d, g, h, n, y, d, e, j, k. Synonym: pr160gag-pol. Ec: 3.4.23.16,2.7.7.49,2.7.7.7,3.1.26.13,3.1.13.2,2.7.7.-,3.1.-.-. Engineered: yes. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase a. Chain: j. Synonym: ppiase a,cyclophilin a,cyclosporin a-binding protein, rotamase a.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Human immunodeficiency virus 1. Organism_taxid: 11676. Gene: gag-pol. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ppia, cypa.
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Ni,S.Gerard,G.Zhao,J.Ning,P.Zhang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
T.Ni
et al.
(2020).
Intrinsic curvature of the HIV-1 CA hexamer underlies capsid topology and interaction with cyclophilin A.
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
27,
855-862.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Mar-20
|
Release date:
|
19-Aug-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P04591
(GAG_HV1H2) -
Gag polyprotein from Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate HXB2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
500 a.a.
146 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P04591
(GAG_HV1H2) -
Gag polyprotein from Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate HXB2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
500 a.a.
220 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.2.7.7.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.2.7.7.49
- RNA-directed Dna polymerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
DNA(n) + a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate = DNA(n+1) + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 DNA(n)
DNA(n)
|
+
|
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate
|
=
|
DNA(n+1)
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.2.7.7.7
- DNA-directed Dna polymerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
DNA(n) + a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate = DNA(n+1) + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 DNA(n)
DNA(n)
|
+
|
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate
|
=
|
DNA(n+1)
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.3.1.-.-
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.3.1.13.2
- exoribonuclease H.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Exonucleolytic cleavage to 5'-phosphomonoester oligonucleotides in both 5'- to 3'- and 3'- to 5'-directions.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.3.1.26.13
- retroviral ribonuclease H.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 7:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, G, H, N, Y, d, e, j, k:
E.C.3.4.23.16
- HIV-1 retropepsin.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Specific for a P1 residue that is hydrophobic, and P1' variable, but often Pro.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 8:
|
 |
Chain J:
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
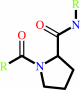 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
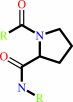 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Struct Mol Biol
27:855-862
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Intrinsic curvature of the HIV-1 CA hexamer underlies capsid topology and interaction with cyclophilin A.
|
|
T.Ni,
S.Gerard,
G.Zhao,
K.Dent,
J.Ning,
J.Zhou,
J.Shi,
J.Anderson-Daniels,
W.Li,
S.Jang,
A.N.Engelman,
C.Aiken,
P.Zhang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The mature retrovirus capsid consists of a variably curved lattice of capsid
protein (CA) hexamers and pentamers. High-resolution structures of the curved
assembly, or in complex with host factors, have not been available. By devising
cryo-EM methodologies for exceedingly flexible and pleomorphic assemblies, we
have determined cryo-EM structures of apo-CA hexamers and in complex with
cyclophilin A (CypA) at near-atomic resolutions. The CA hexamers are
intrinsically curved, flexible and asymmetric, revealing the capsomere and not
the previously touted dimer or trimer interfaces as the key contributor to
capsid curvature. CypA recognizes specific geometries of the curved lattice,
simultaneously interacting with three CA protomers from adjacent hexamers via
two noncanonical interfaces, thus stabilizing the capsid. By determining
multiple structures from various helical symmetries, we further revealed the
essential plasticity of the CA molecule, which allows formation of continuously
curved conical capsids and the mechanism of capsid pattern sensing by CypA.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| |

