 |
PDBsum entry 6y5c
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of glycogen phosphorylase in complex with 52
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form. Chain: a. Synonym: myophosphorylase. Ec: 2.4.1.1
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Oryctolagus cuniculus. Rabbit. Organism_taxid: 9986
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.170
|
R-free:
|
0.211
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Kyriakis,S.M.Koulas,V.T.Skamnaki,D.D.Leonidas
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
B.A.Chetter
et al.
(2020).
Synthetic flavonoid derivatives targeting the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor site: QM/MM-PBSA motivated synthesis of substituted 5,7-dihydroxyflavones, crystallography, in vitro kinetics and ex-vivo cellular experiments reveal novel potent inhibitors.
Bioorg Chem,
102,
104003.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Feb-20
|
Release date:
|
19-Aug-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00489
(PYGM_RABIT) -
Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form from Oryctolagus cuniculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
843 a.a.
809 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.1
- glycogen phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Glycogen
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n) + phosphate = [(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n-1) + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n)
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n-1)
|
+
|
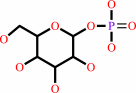 alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Bioorg Chem
102:104003
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Synthetic flavonoid derivatives targeting the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor site: QM/MM-PBSA motivated synthesis of substituted 5,7-dihydroxyflavones, crystallography, in vitro kinetics and ex-vivo cellular experiments reveal novel potent inhibitors.
|
|
B.A.Chetter,
E.Kyriakis,
D.Barr,
A.G.Karra,
E.Katsidou,
S.M.Koulas,
V.T.Skamnaki,
T.J.Snape,
A.G.Psarra,
D.D.Leonidas,
J.M.Hayes.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glycogen phosphorylase (GP) is an important target for the development of new
anti-hyperglycaemic agents. Flavonoids are novel inhibitors of GP, but their
mode of action is unspecific in terms of the GP binding sites involved. Towards
design of synthetic flavonoid analogues acting specifically at the inhibitor
site and to exploit the site's hydrophobic pocket, chrysin has been employed as
a lead compound for the in silico screening of 1169 new analogues with different
B ring substitutions. QM/MM-PBSA binding free energy calculations guided the
final selection of eight compounds, subsequently synthesised using a
Baker-Venkataraman rearrangement-cyclisation approach. Kinetics experiments
against rabbit muscle GPa and GPb together with human liver GPa, revealed three
of these compounds (11, 20 and 43) among the most potent that bind at the site
(Ki s < 4 µM for all three isoforms), and more potent than
previously reported natural flavonoid inhibitors. Multiple inhibition studies
revealed binding exclusively at the inhibitor site. The binding is synergistic
with glucose suggesting that inhibition could be regulated by blood glucose
levels and would decrease as normoglycaemia is achieved. Compound 43 was an
effective inhibitor of glycogenolysis in hepatocytes
(IC50 = 70 µM), further promoting these compounds for
optimization of their drug-like potential. X-ray crystallography studies
revealed the B-ring interactions responsible for the observed potencies.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

