 |
PDBsum entry 6x9c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6x9c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.88
- L-glutamate gamma-semialdehyde dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + NAD+ + H2O = L-glutamate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
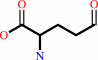 L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 88.89% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
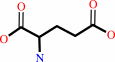 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.5.2
- proline dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-proline + a quinone = (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + a quinol + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
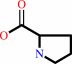 L-proline
L-proline
|
+
|
quinone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
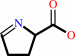 (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
(S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
|
+
|
quinol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FDA)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Arch Biochem Biophys
698:108727
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural analysis of prolines and hydroxyprolines binding to the l-glutamate-γ-semialdehyde dehydrogenase active site of bifunctional proline utilization A.
|
|
A.C.Campbell,
A.N.Bogner,
Y.Mao,
D.F.Becker,
J.J.Tanner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Proline utilization A (PutA) proteins are bifunctional proline catabolic enzymes
that catalyze the 4-electron oxidation of l-proline to l-glutamate using
spatially-separated proline dehydrogenase and l-glutamate-γ-semialdehyde
dehydrogenase (GSALDH, a.k.a. ALDH4A1) active sites. The observation that
l-proline inhibits both the GSALDH activity of PutA and monofunctional GSALDHs
motivated us to study the inhibition of PutA by proline stereoisomers and
analogs. Here we report five high-resolution crystal structures of PutA with the
following ligands bound in the GSALDH active site: d-proline,
trans-4-hydroxy-d-proline, cis-4-hydroxy-d-proline, l-proline, and
trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline. Three of the structures are of ternary complexes of
the enzyme with an inhibitor and either NAD+ or NADH. To our
knowledge, the NADH complex is the first for any GSALDH. The structures reveal a
conserved mode of recognition of the inhibitor carboxylate, which results in the
pyrrolidine rings of the d- and l-isomers having different orientations and
different hydrogen bonding environments. Activity assays show that the compounds
are weak inhibitors with millimolar inhibition constants. Curiously, although
the inhibitors occupy the aldehyde binding site, kinetic measurements show the
inhibition is uncompetitive. Uncompetitive inhibition may involve proline
binding to a remote site or to the enzyme-NADH complex. Together, the structural
and kinetic data expand our understanding of how proline-like molecules interact
with GSALDH, reveal insight into the relationship between stereochemistry and
inhibitor affinity, and demonstrate the pitfalls of inferring the mechanism of
inhibition from crystal structures alone.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

