 |
PDBsum entry 6w4c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6w4c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.3.15
- (S)-2-hydroxy-acid oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate + O2 = a 2-oxocarboxylate + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
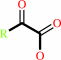 2-oxocarboxylate
2-oxocarboxylate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.3.5
- glyoxylate oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
glyoxylate + O2 + H2O = oxalate + H2O2 + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
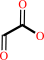 glyoxylate
glyoxylate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
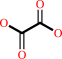 oxalate
oxalate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
64:6730-6744
(2021)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Discovery of Novel, Potent Inhibitors of Hydroxy Acid Oxidase 1 (HAO1) Using DNA-Encoded Chemical Library Screening.
|
|
E.C.Y.Lee,
A.J.McRiner,
K.E.Georgiadis,
J.Liu,
Z.Wang,
A.D.Ferguson,
B.Levin,
M.von Rechenberg,
C.D.Hupp,
M.I.Monteiro,
A.D.Keefe,
A.Olszewski,
C.J.Eyermann,
P.Centrella,
Y.Liu,
S.Arora,
J.W.Cuozzo,
Y.Zhang,
M.A.Clark,
C.Huguet,
A.Kohlmann.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Inhibition of hydroxy acid oxidase 1 (HAO1) is a strategy to mitigate the
accumulation of toxic oxalate that results from reduced activity of
alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGXT) in primary hyperoxaluria 1 (PH1)
patients. DNA-Encoded Chemical Library (DECL) screening provided two novel
chemical series of potent HAO1 inhibitors, represented by compounds
3-6. Compound 5 was further optimized via various
structure-activity relationship (SAR) exploration methods to 29, a
compound with improved potency and absorption, distribution, metabolism, and
excretion (ADME)/pharmacokinetic (PK) properties. Since carboxylic
acid-containing compounds are often poorly permeable and have potential active
glucuronide metabolites, we undertook a brief, initial exploration of acid
replacements with the aim of identifying non-acid-containing HAO1 inhibitors.
Structure-based drug design initiated with Compound 5 led to the
identification of a nonacid inhibitor of HAO1, 31, which has weaker
potency and increased permeability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

