 |
PDBsum entry 6u1h
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus d-alanine-d-alanine ligase in complex with adp, phosphate, mg2+ and k+
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
D-alanine--d-alanine ligase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: d-ala-d-ala ligase,d-alanylalanine synthetase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus (strain hb8 / atcc 27634 / dsm 579). Organism_taxid: 300852. Strain: hb8 / atcc 27634 / dsm 579. Gene: ddl, ttha1587. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.221
|
R-free:
|
0.265
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.L.Pederick,J.B.Bruning
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.L.Pederick
et al.
(2020).
d-Alanine-d-alanine ligase as a model for the activation of ATP-grasp enzymes by monovalent cations.
J Biol Chem,
295,
7894-7904.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Aug-19
|
Release date:
|
06-May-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.6.3.2.4
- D-alanine--D-alanine ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis (Part 1)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 D-alanine + ATP = D-alanyl-D-alanine + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
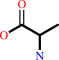 2
×
D-alanine
2
×
D-alanine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
D-alanyl-D-alanine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
295:7894-7904
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
d-Alanine-d-alanine ligase as a model for the activation of ATP-grasp enzymes by monovalent cations.
|
|
J.L.Pederick,
A.P.Thompson,
S.G.Bell,
J.B.Bruning.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The ATP-grasp superfamily of enzymes shares an atypical nucleotide-binding site
known as the ATP-grasp fold. These enzymes are involved in many biological
pathways in all domains of life. One ATP-grasp enzyme, d-alanine-d-alanine
ligase (Ddl), catalyzes ATP-dependent formation of the d-alanyl-d-alanine
dipeptide essential for bacterial cell wall biosynthesis and is therefore an
important antibiotic drug target. Ddl is activated by the monovalent cation
(MVC) K+, but despite its clinical relevance and decades of research,
how this activation occurs has not been elucidated. We demonstrate here that
activating MVCs bind adjacent to the active site of Ddl from Thermus
thermophilus and used a combined biochemical and structural approach to
characterize MVC activation. We found that TtDdl is a type II
MVC-activated enzyme, retaining activity in the absence of MVCs. However, the
efficiency of TtDdl increased ∼20-fold in the presence of activating
MVCs, and it was maximally activated by K+ and Rb+ ions. A
strict dependence on ionic radius of the MVC was observed, with Li+
and Na+ providing little to no TtDdl activation. To understand
the mechanism of MVC activation, we solved crystal structures of TtDdl
representing distinct catalytic stages in complex with K+,
Rb+, or Cs+ Comparison of these structures with apo
TtDdl revealed no evident conformational change on MVC binding. Of note,
the identified MVC binding site is structurally conserved within the ATP-grasp
superfamily. We propose that MVCs activate Ddl by altering the charge
distribution of its active site. These findings provide insight into the
catalytic mechanism of ATP-grasp enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

