 |
PDBsum entry 6tqw

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6tqw
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.17.4.1
- ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-disulfide + H2O = a ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
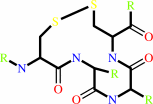 thioredoxin disulfide
thioredoxin disulfide
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
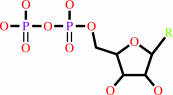 ribonucleoside diphosphate
ribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
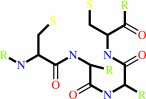 thioredoxin
thioredoxin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(3+) or adenosylcob(III)alamin or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(3+)
|
or
|
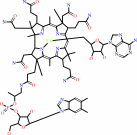 adenosylcob(III)alamin
adenosylcob(III)alamin
|
or
|
Mn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Inorg Chem
25:571-582
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The Bacillus anthracis class Ib ribonucleotide reductase subunit NrdF intrinsically selects manganese over iron.
|
|
K.Grāve,
J.J.Griese,
G.Berggren,
M.D.Bennett,
M.Högbom.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Correct protein metallation in the complex mixture of the cell is a prerequisite
for metalloprotein function. While some metals, such as Cu, are commonly
chaperoned, specificity towards metals earlier in the Irving-Williams series is
achieved through other means, the determinants of which are poorly understood.
The dimetal carboxylate family of proteins provides an intriguing example, as
different proteins, while sharing a common fold and the same 4-carboxylate
2-histidine coordination sphere, are known to require either a Fe/Fe, Mn/Fe or
Mn/Mn cofactor for function. We previously showed that the R2lox proteins from
this family spontaneously assemble the heterodinuclear Mn/Fe cofactor. Here we
show that the class Ib ribonucleotide reductase R2 protein from Bacillus
anthracis spontaneously assembles a Mn/Mn cofactor in vitro, under both aerobic
and anoxic conditions, when the metal-free protein is subjected to incubation
with MnII and FeII in equal concentrations. This
observation provides an example of a protein scaffold intrinsically predisposed
to defy the Irving-Williams series and supports the assumption that the Mn/Mn
cofactor is the biologically relevant cofactor in vivo. Substitution of a second
coordination sphere residue changes the spontaneous metallation of the protein
to predominantly form a heterodinuclear Mn/Fe cofactor under aerobic conditions
and a Mn/Mn metal center under anoxic conditions. Together, the results describe
the intrinsic metal specificity of class Ib RNR and provide insight into control
mechanisms for protein metallation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

