 |
PDBsum entry 6tae

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6tae
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Neutron structure of ferric ascorbate peroxidase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Ascorbate peroxidase. Chain: a. Synonym: cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 1,uncharacterized protein. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Glycine max. Soybean. Organism_taxid: 3847. Gene: apx1, glyma_u021900. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.147
|
R-free:
|
0.189
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Kwon,J.Basran,J.M.Devos,T.E.Schrader,A.Ostermann,M.P.Blakeley, E.L.Raven,P.C.E.Moody
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Kwon
et al.
(2020).
Visualizing the protons in a metalloenzyme electron proton transfer pathway.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
117,
6484-6490.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Oct-19
|
Release date:
|
18-Mar-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q43758
(Q43758_SOYBN) -
L-ascorbate peroxidase from Glycine max
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
250 a.a.
249 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.11.1.11
- L-ascorbate peroxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-ascorbate + H2O2 = L-dehydroascorbate + 2 H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
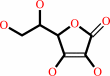 L-ascorbate
L-ascorbate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
=
|
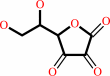 L-dehydroascorbate
L-dehydroascorbate
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Heme
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Heme
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
HEM)
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
117:6484-6490
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Visualizing the protons in a metalloenzyme electron proton transfer pathway.
|
|
H.Kwon,
J.Basran,
J.M.Devos,
R.Suardíaz,
M.W.van der Kamp,
A.J.Mulholland,
T.E.Schrader,
A.Ostermann,
M.P.Blakeley,
P.C.E.Moody,
E.L.Raven.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In redox metalloenzymes, the process of electron transfer often involves the
concerted movement of a proton. These processes are referred to as
proton-coupled electron transfer, and they underpin a wide variety of biological
processes, including respiration, energy conversion, photosynthesis, and
metalloenzyme catalysis. The mechanisms of proton delivery are incompletely
understood, in part due to an absence of information on exact proton locations
and hydrogen bonding structures in a bona fide metalloenzyme proton pathway.
Here, we present a 2.1-Å neutron crystal structure of the complex formed
between a redox metalloenzyme (ascorbate peroxidase) and its reducing substrate
(ascorbate). In the neutron structure of the complex, the protonation states of
the electron/proton donor (ascorbate) and all of the residues involved in the
electron/proton transfer pathway are directly observed. This information sheds
light on possible proton movements during heme-catalyzed oxygen activation, as
well as on ascorbate oxidation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

