 |
PDBsum entry 6t5c
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
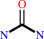 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biophys J
119:1513-1524
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Isoform-Selective Enzyme Inhibitors by Exploring Pocket Size According to the Lock-and-Key Principle.
|
|
V.Dudutienė,
A.Zubrienė,
V.Kairys,
A.Smirnov,
J.Smirnovienė,
J.Leitans,
A.Kazaks,
K.Tars,
L.Manakova,
S.Gražulis,
D.Matulis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In the design of high-affinity and enzyme isoform-selective inhibitors, we
applied an approach of augmenting the substituents attached to the
benzenesulfonamide scaffold in three ways, namely, substitutions at the 3,5- or
2,4,6-positions or expansion of the condensed ring system. The increased size of
the substituents determined the spatial limitations of the active sites of the
12 catalytically active human carbonic anhydrase (CA) isoforms until no binding
was observed because of the inability of the compounds to fit in the active
site. This approach led to the discovery of high-affinity and high-selectivity
compounds for the anticancer target CA IX and antiobesity target CA VB. The
x-ray crystallographic structures of compounds bound to CA IX showed the
positions of the bound compounds, whereas computational modeling confirmed that
steric clashes prevent the binding of these compounds to other isoforms and thus
avoid undesired side effects. Such an approach, based on the Lock-and-Key
principle, could be used for the development of enzyme-specific drug candidate
compounds.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

