 |
PDBsum entry 6svh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Peptide binding protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6svh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
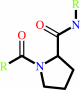 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
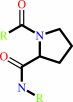 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
59:22132-22139
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Protein Allostery at Atomic Resolution.
|
|
D.Strotz,
J.Orts,
H.Kadavath,
M.Friedmann,
D.Ghosh,
S.Olsson,
C.N.Chi,
A.Pokharna,
P.Güntert,
B.Vögeli,
R.Riek.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Protein allostery is a phenomenon involving the long range coupling between two
distal sites in a protein. In order to elucidate allostery at atomic resoluion
on the ligand-binding WW domain of the enzyme Pin1, multistate structures were
calculated from exact nuclear Overhauser effect (eNOE). In its free form, the
protein undergoes a microsecond exchange between two states, one of which is
predisposed to interact with its parent catalytic domain. In presence of the
positive allosteric ligand, the equilibrium between the two states is shifted
towards domain-domain interaction, suggesting a population shift model. In
contrast, the allostery-suppressing ligand decouples the side-chain arrangement
at the inter-domain interface thereby reducing the inter-domain interaction. As
such, this mechanism is an example of dynamic allostery. The presented distinct
modes of action highlight the power of the interplay between dynamics and
function in the biological activity of proteins.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

