 |
PDBsum entry 6qkt
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.8.1.3
- haloacetate dehalogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a haloacetate + H2O = a halide anion + glycolate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
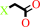 haloacetate
haloacetate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
halide anion
|
+
|
glycolate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
141:11540-11556
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate-Based Allosteric Regulation of a Homodimeric Enzyme.
|
|
P.Mehrabi,
C.Di Pietrantonio,
T.H.Kim,
A.Sljoka,
K.Taverner,
C.Ing,
N.Kruglyak,
R.Pomès,
E.F.Pai,
R.S.Prosser.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Many enzymes operate through half-of-the sites reactivity wherein a single
protomer is catalytically engaged at one time. In the case of the homodimeric
enzyme, fluoroacetate dehalogenase, substrate binding triggers closing of a
regulatory cap domain in the empty protomer, preventing substrate access to the
remaining active site. However, the empty protomer serves a critical role by
acquiring more disorder upon substrate binding, thereby entropically favoring
the forward reaction. Empty protomer dynamics are also allosterically coupled to
the bound protomer, driving conformational exchange at the active site and
progress along the reaction coordinate. Here, we show that at high
concentrations, a second substrate binds along the substrate-access channel of
the occupied protomer, thereby dampening interprotomer dynamics and inhibiting
catalysis. While a mutation (K152I) abrogates second site binding and removes
inhibitory effects, it also precipitously lowers the maximum catalytic rate,
implying a role for the allosteric pocket at low substrate concentrations, where
only a single substrate engages the enzyme at one time. We show that this outer
pocket first desolvates the substrate, whereupon it is deposited in the active
site. Substrate binding to the active site then triggers the empty outer pocket
to serve as an interprotomer allosteric conduit, enabling enhanced dynamics and
sampling of activation states needed for catalysis. These allosteric networks
and the ensuing changes resulting from second substrate binding are delineated
using rigidity-based allosteric transmission theory and validated by nuclear
magnetic resonance and functional studies. The results illustrate the role of
dynamics along allosteric networks in facilitating function.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

