 |
PDBsum entry 6ppt
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Chaperone
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural basis for client recognition and activity of hsp40 chaperones
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Alkaline phosphatase,chaperone protein dnaj 2 fusion. Chain: a. Synonym: apase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli (strain k12), thermus thermophilus (strain hb8 / atcc 27634 / dsm 579). Organism_taxid: 83333, 300852. Strain: k12, hb8 / atcc 27634 / dsm 579. Gene: phoa, b0383, jw0374, dnaj2, ttha1489. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
NMR struc:
|
 |
20 models
|
 |
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Jiang,P.Rossi,C.G.Kalodimos
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.Jiang
et al.
(2019).
Structural basis for client recognition and activity of Hsp40 chaperones.
Science,
365,
1313-1319.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Jul-19
|
Release date:
|
18-Sep-19
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.1
- alkaline phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a phosphate monoester + H2O = an alcohol + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
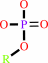 phosphate monoester
phosphate monoester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 alcohol
alcohol
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+); Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Science
365:1313-1319
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for client recognition and activity of Hsp40 chaperones.
|
|
Y.Jiang,
P.Rossi,
C.G.Kalodimos.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Hsp70 and Hsp40 chaperones work synergistically in a wide range of biological
processes including protein synthesis, membrane translocation, and folding. We
used nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to determine the solution structure
and dynamic features of an Hsp40 in complex with an unfolded client protein.
Atomic structures of the various binding sites in the client complexed to the
binding domains of the Hsp40 reveal the recognition pattern. Hsp40 engages the
client in a highly dynamic fashion using a multivalent binding mechanism that
alters the folding properties of the client. Different Hsp40 family members have
different numbers of client-binding sites with distinct sequence selectivity,
providing additional mechanisms for activity regulation and function
modification. Hsp70 binding to Hsp40 displaces the unfolded client. The activity
of Hsp40 is altered in its complex with Hsp70, further regulating client binding
and release.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

