 |
PDBsum entry 6lrh
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.3.27
- arginine dihydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-arginine + 2 H2O + 2 H+ = L-ornithine + 2 NH4+ + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 L-arginine
L-arginine
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
=
|
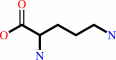 L-ornithine
L-ornithine
|
+
|
2
×
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.12
- ornithine cyclodeaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-ornithine = L-proline + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 L-ornithine
L-ornithine
|
=
|
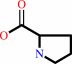 2
×
L-proline
2
×
L-proline
|
+
|
2
×
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
NAD(+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
295:5751-5760
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and mutational analyses of the bifunctional arginine dihydrolase and ornithine cyclodeaminase AgrE from the cyanobacterium Anabaena.
|
|
H.Lee,
S.Rhee.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In cyanobacteria, metabolic pathways that use the nitrogen-rich amino acid
arginine play a pivotal role in nitrogen storage and mobilization. The
N-terminal domains of two recently identified bacterial enzymes: ArgZ from
Synechocystis and AgrE from Anabaena, have been found to contain
an arginine dihydrolase. This enzyme provides catabolic activity that converts
arginine to ornithine, resulting in concomitant release of CO2 and
ammonia. In Synechocystis, the ArgZ-mediated ornithine-ammonia cycle
plays a central role in nitrogen storage and remobilization. The C-terminal
domain of AgrE contains an ornithine cyclodeaminase responsible for the
formation of proline from ornithine and ammonia production, indicating that AgrE
is a bifunctional enzyme catalyzing two sequential reactions in arginine
catabolism. Here, the crystal structures of AgrE in three different ligation
states revealed that it has a tetrameric conformation, possesses a binding site
for the arginine dihydrolase substrate l-arginine and product l-ornithine, and
contains a binding site for the coenzyme NAD(H) required for ornithine
cyclodeaminase activity. Structure-function analyses indicated that the
structure and catalytic mechanism of arginine dihydrolase in AgrE are highly
homologous with those of a known bacterial arginine hydrolase. We found that in
addition to other active-site residues, Asn-71 is essential for AgrE's
dihydrolase activity. Further analysis suggested the presence of a passage for
substrate channeling between the two distinct AgrE active sites, which are
situated ∼45 Å apart. These results provide structural and functional
insights into the bifunctional arginine dihydrolase-ornithine cyclodeaminase
enzyme AgrE required for arginine catabolism in Anabaena.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

