 |
PDBsum entry 6l9c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6l9c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Neutron structure of copper amine oxidase from arthrobacter glibiformis at pd 7.4
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phenylethylamine oxidase. Chain: x. Synonym: primary amine oxidase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arthrobacter globiformis. Organism_taxid: 1665. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.14Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.168
|
R-free:
|
0.182
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Murakawa,K.Kurihara,M.Shoji,C.Shibazaki,T.Sunami,T.Tamada,N.Yano, T.Yamada,K.Kusaka,M.Suzuki,Y.Shigeta,R.Kuroki,H.Hayashi,Y.Yano, K.Tanizawa,M.Adachi,T.Okajima
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
T.Murakawa
et al.
(2020).
Neutron crystallography of copper amine oxidase reveals keto/enolate interconversion of the quinone cofactor and unusual proton sharing.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
117,
10818-10824.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Nov-19
|
Release date:
|
29-Apr-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P46881
(PAOX_ARTGO) -
Phenylethylamine oxidase from Arthrobacter globiformis
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
638 a.a.
622 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.21
- primary-amine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a primary methyl amine + O2 + H2O = an aldehyde + H2O2 + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
primary methyl amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
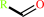 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
117:10818-10824
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Neutron crystallography of copper amine oxidase reveals keto/enolate interconversion of the quinone cofactor and unusual proton sharing.
|
|
T.Murakawa,
K.Kurihara,
M.Shoji,
C.Shibazaki,
T.Sunami,
T.Tamada,
N.Yano,
T.Yamada,
K.Kusaka,
M.Suzuki,
Y.Shigeta,
R.Kuroki,
H.Hayashi,
T.Yano,
K.Tanizawa,
M.Adachi,
T.Okajima.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Recent advances in neutron crystallographic studies have provided structural
bases for quantum behaviors of protons observed in enzymatic reactions. Thus, we
resolved the neutron crystal structure of a bacterial copper (Cu) amine oxidase
(CAO), which contains a prosthetic Cu ion and a protein-derived redox cofactor,
topa quinone (TPQ). We solved hitherto unknown structures of the active site,
including a keto/enolate equilibrium of the cofactor with a nonplanar quinone
ring, unusual proton sharing between the cofactor and the catalytic base, and
metal-induced deprotonation of a histidine residue that coordinates to the Cu.
Our findings show a refined active-site structure that gives detailed
information on the protonation state of dissociable groups, such as the quinone
cofactor, which are critical for catalytic reactions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

