 |
PDBsum entry 6i2f
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
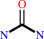 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
ACS Chem Biol
15:675-685
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Conformational Changes in Alkyl Chains Determine the Thermodynamic and Kinetic Binding Profiles of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.
|
|
S.Glöckner,
K.Ngo,
C.P.Sager,
T.Hüfner-Wulsdorf,
A.Heine,
G.Klebe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Thermodynamics and kinetics of protein-ligand binding are both important aspects
for the design of novel drug molecules. Presently, thermodynamic data are
collected with isothermal titration calorimetry, while kinetic data are mostly
derived from surface plasmon resonance. The new method of kinITC provides both
thermodynamic and kinetic data from calorimetric titration measurements. The
present study demonstrates the convenient collection of calorimetric data
suitable for both thermodynamic and kinetic analysis for two series of
congeneric ligands of human carbonic anhydrase II and correlates these findings
with structural data obtained by macromolecular crystallography to shed light on
the importance of shape complementarity for thermodynamics and kinetics
governing a protein-ligand binding event. The study shows how minute chemical
alterations change preferred ligand conformation and can be used to manipulate
thermodynamic and kinetic signatures of binding. They give rise to the
observation that analogous n-alkyl and n-alkyloxy derivatives of
identical chain length swap their binding kinetic properties at unchanged
binding affinity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

