 |
PDBsum entry 6fwc
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Flavoprotein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human monoamine oxidase b (mao b) in complex with fluorophenyl-chromone-carboxamide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] b. Chain: a, b. Synonym: monoamine oxidase type b,mao-b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: maob. Expressed in: komagataella pastoris. Expression_system_taxid: 4922
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.162
|
R-free:
|
0.189
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Reis,N.Manzella,F.Cagide,J.Mialet-Perez,E.Uriarte,A.Parini, F.Borges,C.Binda
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Reis
et al.
(2018).
Tight-Binding Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase B by Chromone Analogs: A Kinetic, Crystallographic, and Biological Analysis.
J Med Chem,
61,
4203-4212.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
06-Mar-18
|
Release date:
|
25-Apr-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P27338
(AOFB_HUMAN) -
Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
520 a.a.
499 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.21
- primary-amine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a primary methyl amine + O2 + H2O = an aldehyde + H2O2 + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
primary methyl amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
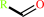 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.4
- monoamine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a secondary aliphatic amine + O2 + H2O = a primary amine + an aldehyde + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
secondary aliphatic amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
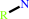 primary amine
primary amine
|
+
|
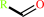 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
61:4203-4212
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Tight-Binding Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase B by Chromone Analogs: A Kinetic, Crystallographic, and Biological Analysis.
|
|
J.Reis,
N.Manzella,
F.Cagide,
J.Mialet-Perez,
E.Uriarte,
A.Parini,
F.Borges,
C.Binda.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is a validated drug target for Parkinson's disease.
Chromone derivatives were identified as novel potent and reversible MAO-B
inhibitors, and herewith we report on a crystallographic and biochemical
analysis to investigate their inhibition mechanism. The crystal structures of
human MAO-B in complex with three chromone analogs bearing different
substituents on the exocyclic aromatic ring (determined at 1.6-1.8 Å
resolution) showed that they all bind in the active site cavity of the protein
with the chromone moiety located in front of the FAD cofactor. These inhibitors
form two hydrogen bonds with Tyr435 and Cys172 and perfectly fit the hydrophobic
flat active site of human MAO-B. This is reflected in their tight-binding
mechanism of inhibition with Ki values of 55, 17, and 31 nM for
N-(3',4'-dimethylphenyl)-4-oxo-4 H-chromene-3-carboxamide (1),
N-(3'-chlorophenyl)-4-oxo-4 H-chromene-3-carboxamide (2), and
N-(3'-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4 H-chromene-3-carboxamide (3), respectively. These
compounds were also 1000-fold more effective than l-deprenyl in reducing the
cellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS).

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

