 |
PDBsum entry 6f6d

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6f6d
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.1.14.11.68
- [histone H3]-trimethyl-L-lysine(27) demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6,N6,N6-trimethyl-L-lysyl27-[histone H3] + 2 2-oxoglutarate + 2 O2 = N6-methyl-L-lysyl27-[histone H3] + 2 formaldehyde + 2 succinate + 2 CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6),N(6),N(6)-trimethyl-L-lysyl(27)-[histone H3]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 2
×
2-oxoglutarate
2
×
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 2
×
O2
2
×
O2
|
=
|
N(6)-methyl-L-lysyl(27)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
2
×
formaldehyde
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 40.00% similarity
|
+
|
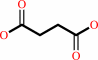 2
×
succinate
2
×
succinate
|
+
|
 2
×
CO2
2
×
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
57:585-592
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Basis of Histone Demethylase KDM6B Histone 3 Lysine 27 Specificity.
|
|
S.E.Jones,
L.Olsen,
M.Gajhede.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
KDM subfamily 6 enzymes KDM6A and KDM6B specifically catalyze demethylation of
di- and trimethylated lysine on histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3/2) and play an
important role in repression of developmental genes. Despite identical amino
acid sequence in the immediate surroundings of H3K9me3/2 (ARKS), the enzymes do
not catalyze demethylation of this general marker of repression. To address this
question for KDM6B, we used computational methods to identify H3(17-33)-derived
peptides with improved binding affinity that would allow co-crystallization with
the catalytic core of human KDM6B (ccKDM6B). A total of five peptides were
identified, and their IC50 values were determined in a
matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight-based assay. Despite
none of the peptides showing affinity significantly higher than that of the
H3(17-33) peptide, it was possible to co-crystallize ccKDM6B with a
H3(17-33)A21M peptide. This structure reveals the interactions between the KDM6B
zinc binding domain and the H3(17-23) region. Although KDM6A and KDM6B differ in
primary sequence, particularly in the H3L20 binding pocket of the zinc binding
domains, where two histidines in KDM6A have been replaced by a glutamate and a
tyrosine, they bind H3(17-23) in a very similar fashion. This structure shows
that KDM6B, in analogy with KDM6A, also uses the zinc binding domain to achieve
H3K27me3/me2 specificity. The histidine to glutamine substitution at amino acid
position 1564 in the KDM6B zinc binding domain can further explain why KDM6B
binds substrates with an affinity higher than that of KDM6A.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

