 |
PDBsum entry 6evd
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.102
- phenacrylate decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
(E)-4-coumarate + H+ = 4-vinylphenol + CO2
|
|
2.
|
(E)-cinnamate + H+ = styrene + CO2
|
|
3.
|
(E)-ferulate + H+ = 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol + CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(E)-4-coumarate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
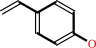 4-vinylphenol
4-vinylphenol
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
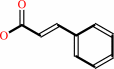 (E)-cinnamate
(E)-cinnamate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
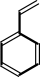 styrene
styrene
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(E)-ferulate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Prenyl-FMNH(2)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
293:2272-2287
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The role of conserved residues in Fdc decarboxylase in prenylated flavin mononucleotide oxidative maturation, cofactor isomerization, and catalysis.
|
|
S.S.Bailey,
K.A.P.Payne,
K.Fisher,
S.A.Marshall,
M.J.Cliff,
R.Spiess,
D.A.Parker,
S.E.J.Rigby,
D.Leys.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The UbiD family of reversible decarboxylases act on aromatic, heteroaromatic,
and unsaturated aliphatic acids and utilize a prenylated flavin mononucleotide
(prFMN) as cofactor, bound adjacent to a conserved Glu-Arg-Glu/Asp ionic network
in the enzyme's active site. It is proposed that UbiD activation requires
oxidative maturation of the cofactor, for which two distinct isomers,
prFMNketimineand prFMNiminium, have been observed. It also
has been suggested that only the prFMNiminiumform is relevant to
catalysis, which requires transient cycloaddition between substrate and
cofactor. UsingAspergillus nigerFdc1 as a model system, we reveal that
isomerization of prFMNiminiumto prFMNketimineis a
light-dependent process that is largely independent of the
Glu277-Arg173-Glu282network and accompanied by
irreversible loss of activity. On the other hand, efficient catalysis was highly
dependent on an intact Glu-Arg-Glu network, as only Glu → Asp substitutions
retain activity. Surprisingly, oxidative maturation to form the
prFMNiminiumspecies is severely affected only for the R173A variant.
In summary, the unusual irreversible isomerization of prFMN is light-dependent
and probably proceeds via high-energy intermediates but is independent of the
Glu-Arg-Glu network. Our results from mutagenesis, crystallographic,
spectroscopic, and kinetic experiments indicate a clear role for the Glu-Arg-Glu
network in both catalysis and oxidative maturation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

