 |
PDBsum entry 6b5h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6b5h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Aldh1a2 liganded with NAD and 1-(4-cyanophenyl)-n-(3-fluorophenyl)-3- [4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-1h-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (compound cm121)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Retinal dehydrogenase 2. Chain: a, b, c, d. Fragment: unp residues 26-518. Synonym: raldh2, aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member a2, retinaldehyde-specific dehydrogenase type 2, raldh(ii). Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: aldh1a2, raldh2. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.207
|
R-free:
|
0.264
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Chen,J.-Y.Zhu,E.Schonbrunn
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.Chen
et al.
(2018).
Structural Basis of ALDH1A2 Inhibition by Irreversible and Reversible Small Molecule Inhibitors.
ACS Chem Biol,
13,
582-590.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Sep-17
|
Release date:
|
10-Jan-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O94788
(AL1A2_HUMAN) -
Retinal dehydrogenase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
518 a.a.
492 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.36
- retinal dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
retinal + NAD+ + H2O = retinoate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
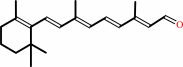 retinal
retinal
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
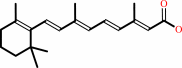 retinoate
retinoate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
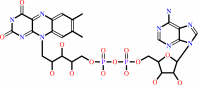 FAD
FAD
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
ACS Chem Biol
13:582-590
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Basis of ALDH1A2 Inhibition by Irreversible and Reversible Small Molecule Inhibitors.
|
|
Y.Chen,
J.Y.Zhu,
K.H.Hong,
D.C.Mikles,
G.I.Georg,
A.S.Goldstein,
J.K.Amory,
E.Schönbrunn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Enzymes of the ALDH1A subfamily of aldehyde dehydrogenases are crucial in
regulating retinoic acid (RA) signaling and have received attention as potential
drug targets. ALDH1A2 is the primary RA-synthesizing enzyme in mammalian
spermatogenesis and is therefore considered a viable drug target for male
contraceptive development. However, only a small number of ALDH1A2 inhibitors
have been reported, and information on the structure of ALDH1A2 was limited to
the NAD-liganded enzyme void of substrate or inhibitors. Herein, we describe the
mechanism of action of structurally unrelated reversible and irreversible
inhibitors of human ALDH1A2 using direct binding studies and X-ray
crystallography. All inhibitors bind to the active sites of tetrameric ALDH1A2.
Compound WIN18,446 covalently reacts with the side chain of the catalytic
residue Cys320, resulting in a chiral adduct in ( R) configuration. The covalent
adduct directly affects the neighboring NAD molecule, which assumes a contracted
conformation suboptimal for the dehydrogenase reaction. The reversible
inhibitors interact predominantly through direct hydrogen bonding interactions
with residues in the vicinity of Cys320 without affecting NAD. Upon interaction
with inhibitors, a large flexible loop assumes regular structure, thereby
shielding the active site from solvent. The precise knowledge of the binding
modes provides a new framework for the rational design of novel inhibitors of
ALDH1A2 with improved potency and selectivity profiles.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

