 |
PDBsum entry 5zmd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/DNA
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5zmd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/DNA
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of fto in complex with m6da modified ssdna
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase fto. Chain: a, c, e, g. Synonym: fat mass and obesity-associated protein. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. DNA (5'-d(p Tp Cp Tp (6Ma)p Tp Ap Tp Cp G)-3'). Chain: b, d, f, h. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: fto, kiaa1752. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Synthetic: yes. DNA launch vector pde-gfp2. Organism_taxid: 415098
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.272
|
R-free:
|
0.292
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
X.Zhang,L.H.Wei,J.Luo,Y.Xiao,J.Liu,W.Zhang,L.Zhang,G.F.Jia
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
X.Zhang
et al.
(2019).
Structural insights into FTO's catalytic mechanism for the demethylation of multiple RNA substrates.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
116,
2919-2924.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-Apr-18
|
Release date:
|
10-Apr-19
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9C0B1
(FTO_HUMAN) -
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
505 a.a.
402 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
T-C-T-6MA-T-A-T-C-G
9 bases
|
|
|
|
T-C-T-6MA-T-A-T-C-G
9 bases
|
|
|
|
T-C-T-6MA-T-A-T-C-G
9 bases
|
|
|
|
T-C-T-6MA-T-A-T-C-G
9 bases
|
|

|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.53
- mRNA N(6)-methyladenine demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an N6-methyladenosine in mRNA + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = an adenosine in mRNA + formaldehyde + succinate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-methyladenosine in mRNA
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
adenosine in mRNA
|
+
|
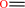 formaldehyde
formaldehyde
|
+
|
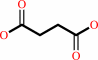 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(3+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
116:2919-2924
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural insights into FTO's catalytic mechanism for the demethylation of multiple RNA substrates.
|
|
X.Zhang,
L.H.Wei,
Y.Wang,
Y.Xiao,
J.Liu,
W.Zhang,
N.Yan,
G.Amu,
X.Tang,
L.Zhang,
G.Jia.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
FTO demethylates internal N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
and N6,2'-O-dimethyladenosine
(m6Am; at the cap +1 position) in mRNA, m6A and
m6Am in snRNA, and N1-methyladenosine
(m1A) in tRNA in vivo, and in vitro evidence supports that it can
also demethylate N6-methyldeoxyadenosine (6mA),
3-methylthymine (3mT), and 3-methyluracil (m3U). However, it remains
unclear how FTO variously recognizes and catalyzes these diverse substrates.
Here we demonstrate-in vitro and in vivo-that FTO has extensive demethylation
enzymatic activity on both internal m6A and cap
m6Am Considering that 6mA, m6A, and
m6Am all share the same nucleobase, we present a crystal
structure of human FTO bound to 6mA-modified ssDNA, revealing the molecular
basis of the catalytic demethylation of FTO toward multiple RNA substrates. We
discovered that (i) N6-methyladenine is the most
favorable nucleobase substrate of FTO, (ii) FTO displays the same
demethylation activity toward internal m6A and
m6Am in the same RNA sequence, suggesting that the
substrate specificity of FTO primarily results from the interaction of residues
in the catalytic pocket with the nucleobase (rather than the ribose ring), and
(iii) the sequence and the tertiary structure of RNA can affect the
catalytic activity of FTO. Our findings provide a structural basis for
understanding the catalytic mechanism through which FTO demethylates its
multiple substrates and pave the way forward for the structure-guided design of
selective chemicals for functional studies and potential therapeutic
applications.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

